TLR/WNT: A Novel Relationship in Immunomodulation of Lung Cancer
- PMID: 35742983
- PMCID: PMC9224119
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126539
TLR/WNT: A Novel Relationship in Immunomodulation of Lung Cancer
Abstract
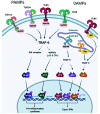
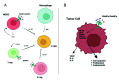
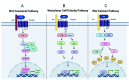
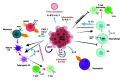
The most frequent cause of death by cancer worldwide is lung cancer, and the 5-year survival rate is still very poor for patients with advanced stage. Understanding the crosstalk between the signaling pathways that are involved in disease, especially in metastasis, is crucial to developing new targeted therapies. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are master regulators of the immune responses, and their dysregulation in lung cancer is linked to immune escape and promotes tumor malignancy by facilitating angiogenesis and proliferation. On the other hand, over-activation of the WNT signaling pathway has been reported in lung cancer and is also associated with tumor metastasis via induction of Epithelial-to-mesenchymal-transition (EMT)-like processes. An interaction between both TLRs and the WNT pathway was discovered recently as it was found that the TLR pathway can be activated by WNT ligands in the tumor microenvironment; however, the implications of such interactions in the context of lung cancer have not been discussed yet. Here, we offer an overview of the interaction of TLR-WNT in the lung and its potential implications and role in the oncogenic process.
Keywords: TLR; WNT; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

