Monocyte-Macrophage Lineage Cell Fusion
- PMID: 35742997
- PMCID: PMC9223484
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126553
Monocyte-Macrophage Lineage Cell Fusion
Abstract
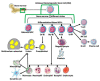
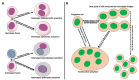
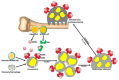
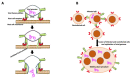
Cell fusion (fusogenesis) occurs in natural and pathological conditions in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Cells of monocyte-macrophage lineage are highly fusogenic. They create syncytial multinucleated giant cells (MGCs) such as osteoclasts (OCs), MGCs associated with the areas of infection/inflammation, and foreign body-induced giant cells (FBGCs). The fusion of monocytes/macrophages with tumor cells may promote cancer metastasis. We describe types and examples of monocyte-macrophage lineage cell fusion and the role of actin-based structures in cell fusion.
Keywords: cell fusion; cell protrusions; giant cells; hematopoietic stem cells; macrophage; monocyte; osteoclast; podosomes; syncytium; tumor-associated macrophages; viral fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bellido T., Plotkin L.I., Bruzzaniti A. Chapter 3—Bone Cells. In: Burr D.B., Allen M.R., editors. Basic and Applied Bone Biology. 2nd ed. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2019. pp. 37–55. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

