Allicin as a Volatile or Nebulisable Antimycotic for the Treatment of Pulmonary Mycoses: In Vitro Studies Using a Lung Flow Test Rig
- PMID: 35743050
- PMCID: PMC9224539
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126607
Allicin as a Volatile or Nebulisable Antimycotic for the Treatment of Pulmonary Mycoses: In Vitro Studies Using a Lung Flow Test Rig
Abstract
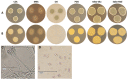
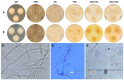
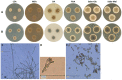
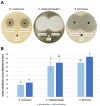
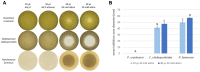
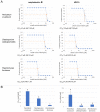
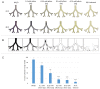
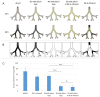
Fungal infections of the lung are an increasing problem worldwide and the search for novel therapeutic agents is a current challenge due to emerging resistance to current antimycotics. The volatile defence substance allicin is formed naturally by freshly injured garlic plants and exhibits broad antimicrobial potency. Chemically synthesised allicin was active against selected fungi upon direct contact and via the gas phase at comparable concentrations to the pharmaceutically used antimycotic amphotericin B. We investigated the suppression of fungal growth by allicin vapour and aerosols in vitro in a test rig at air flow conditions mimicking the human lung. The effect of allicin via the gas phase was enhanced by ethanol. Our results suggest that allicin is a potential candidate for development for use in antifungal therapy for lung and upper respiratory tract infections.
Keywords: Paecilomyces; allicin; antimycotic; lung infection; mycosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Solano Aquilar E., Negroni R., Meinhof W., Padilha-Gonçalves A., Pappagianis D., Iwata K., González Mendoza A., Graybill J.R. Systemic Mycosis. In: Orfanos C.E., Stadler R., Gollnick H., editors. Dermatology in Five Continents. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 1988. pp. 355–376. - DOI
-
- Burns T., Breathnach S.M., Cox N., Griffiths C. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 8th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; New York, NY, USA: 2013.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

