Coronin1C Is a GDP-Specific Rab44 Effector That Controls Osteoclast Formation by Regulating Cell Motility in Macrophages
- PMID: 35743062
- PMCID: PMC9224296
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126619
Coronin1C Is a GDP-Specific Rab44 Effector That Controls Osteoclast Formation by Regulating Cell Motility in Macrophages
Abstract
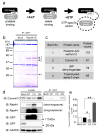
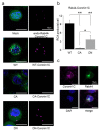
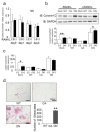
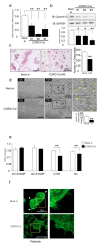
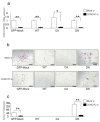
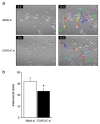
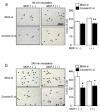
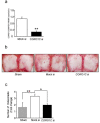
Osteoclasts are multinucleated bone-resorbing cells that are formed by the fusion of macrophages. Recently, we identified Rab44, a large Rab GTPase, as an upregulated gene during osteoclast differentiation that negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation. However, the molecular mechanisms by which Rab44 negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation remain unknown. Here, we found that the GDP form of Rab44 interacted with the actin-binding protein, Coronin1C, in murine macrophages. Immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that the interaction of Rab44 and Coronin1C occurred in wild-type and a dominant-negative (DN) mutant of Rab44, but not in a constitutively active (CA) mutant of Rab44. Consistent with these findings, the expression of the CA mutant inhibited osteoclast differentiation, whereas that of the DN mutant enhanced this differentiation. Using a phase-contrast microscope, Coronin1C-knockdown osteoclasts apparently impaired multinuclear formation. Moreover, Coronin1C knockdown impaired the migration and chemotaxis of RAW-D macrophages. An in vivo experimental system demonstrated that Coronin1C knockdown suppresses osteoclastogenesis. Therefore, the decreased cell formation and fusion of Coronin1C-depleted osteoclasts might be due to the decreased migration of Coronin1C-knockdown macrophages. These results indicate that Coronin1C is a GDP-specific Rab44 effector that controls osteoclast formation by regulating cell motility in macrophages.
Keywords: Coronin1C; Rab44; cell motility; effector; osteoclast differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rab44, a novel large Rab GTPase, negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation by modulating intracellular calcium levels followed by NFATc1 activation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Jan;75(1):33-48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2607-9. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 28791425 Free PMC article.
-
Actin binding LIM 1 (abLIM1) negatively controls osteoclastogenesis by regulating cell migration and fusion.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;234(1):486-499. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26605. Epub 2018 Jun 15. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29904924
-
Dennd2c Negatively Controls Multinucleation and Differentiation in Osteoclasts by Regulating Actin Polymerization and Protrusion Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 25;25(21):11479. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111479. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519032 Free PMC article.
-
Regulators of osteoclast differentiation and cell-cell fusion.Keio J Med. 2011;60(4):101-5. doi: 10.2302/kjm.60.101. Keio J Med. 2011. PMID: 22200633 Review.
-
Regulation of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption by microRNA.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 May 10;79(6):287. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04298-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35536437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rab44 Deficiency Induces Impaired Immune Responses to Nickel Allergy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 4;24(2):994. doi: 10.3390/ijms24020994. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674510 Free PMC article.
-
Abr, a Rho-regulating protein, modulates osteoclastogenesis by enhancing lamellipodia formation by interacting with poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Sep;50(9):7557-7569. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08690-0. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37507586
-
TBC1D1 is an energy-responsive polarization regulator of macrophages via governing ROS production in obesity.Sci China Life Sci. 2024 Sep;67(9):1899-1914. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2628-1. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38902450
References
-
- Takayanagi H., Kim S., Koga T., Nishina H., Isshiki M., Yoshida H., Saiura A., Isobe M., Yokochi T., Inoue J., et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev. Cell. 2002;3:889–901. doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00369-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Okusha Y., Tran M.T., Itagaki M., Sogawa C., Eguchi T., Okui T., Kadowaki T., Sakai E., Tsukuba T., Okamoto K. Rab11A Functions as a Negative Regulator of Osteoclastogenesis through Dictating Lysosome-Induced Proteolysis of c-fms and RANK Surface Receptors. Cells. 2020;9:2384. doi: 10.3390/cells9112384. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

