Comparative Analysis of the Cytotoxic Effect of a Complex of Selenium Nanoparticles Doped with Sorafenib, "Naked" Selenium Nanoparticles, and Sorafenib on Human Hepatocyte Carcinoma HepG2 Cells
- PMID: 35743086
- PMCID: PMC9223423
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126641
Comparative Analysis of the Cytotoxic Effect of a Complex of Selenium Nanoparticles Doped with Sorafenib, "Naked" Selenium Nanoparticles, and Sorafenib on Human Hepatocyte Carcinoma HepG2 Cells
Abstract
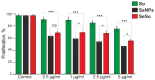
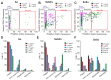
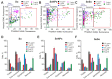
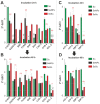
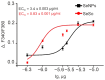
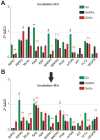
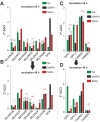
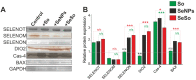
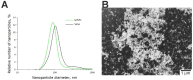
Despite the use of sorafenib as one of the most effective drugs for the treatment of liver cancer, its significant limitations remain-poor solubility, the need to use high doses with the ensuing complications on healthy tissues and organs, and the formation of cell resistance to the drug. At the same time, there is more and more convincing evidence of the anticancer effect of selenium-containing compounds and nanoparticles. The aim of this work was to develop a selenium-sorafenib nanocomplex and study the molecular mechanisms of its anticancer effect on human hepatocyte carcinoma cells, where nanoselenium is not only a sorafenib transporter, but also an active compound. We have created a selenium-sorafenib nanocomplex based on selenium nanoparticles with size 100 nm. Using vitality tests, fluorescence microscopy, and PCR analysis, it was possible to show that selenium nanoparticles, both by themselves and doped with sorafenib, have a pronounced pro-apoptotic effect on HepG2 cells with an efficiency many times greater than that of sorafenib (So). "Naked" selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) and the selenium-sorafenib nanocomplex (SeSo), already after 24 h of exposure, lead to the induction of the early stages of apoptosis with the transition to the later stages with an increase in the incubation time up to 48 h. At the same time, sorafenib, at the studied concentrations, began to exert a proapoptotic effect only after 48 h. Under the action of SeNPs and SeSo, both classical pathways of apoptosis induction and ER-stress-dependent pathways involving Ca2+ ions are activated. Thus, sorafenib did not cause the generation of Ca2+ signals by HepG2 cells, while SeNPs and SeSo led to the activation of the Ca2+ signaling system of cells. At the same time, the selenium-sorafenib nanocomplex turned out to be more effective in activating the Ca2+ signaling system of cells, inducing apoptosis and ER stress by an average of 20-25% compared to "naked" selenium nanoparticles. Our data on the mechanisms of action and the created nanocomplex are promising as a platform for the creation of highly selective and effective drugs with targeted delivery to tumors.
Keywords: apoptosis; calcium signaling; cancer; gene expression; necrosis; selenium nanoparticles; selenium–sorafenib nanocomplex; sorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wilhelm S.M., Carter C., Tang L., Wilkie D., McNabola A., Rong H., Chen C., Zhang X., Vincent P., McHugh M., et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7099–7109. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1443. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

