Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the bZIP Transcription Factor Family in Rice Bakanae Disease Pathogen, Fusarium fujikuroi
- PMID: 35743103
- PMCID: PMC9223689
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126658
Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the bZIP Transcription Factor Family in Rice Bakanae Disease Pathogen, Fusarium fujikuroi
Abstract
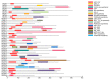
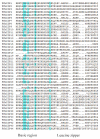
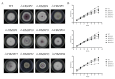
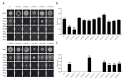
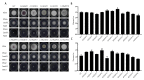
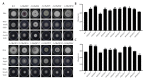
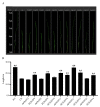
Fungal basic leucine zipper (bZIP) proteins play a vital role in biological processes such as growth, biotic/abiotic stress responses, nutrient utilization, and invasion. In this study, genome-wide identification of bZIP genes in the fungus Fusarium fujikuroi, the pathogen of bakanae disease, was carried out. Forty-four genes encoding bZIP transcription factors (TFs) from the genome of F. fujikuroi (FfbZIP) were identified and functionally characterized. Structures, domains, and phylogenetic relationships of the sequences were analyzed by bioinformatic approaches. Based on the phylogenetic relationships with the FfbZIP proteins of eight other fungi, the bZIP genes can be divided into six groups (A-F). The additional conserved motifs have been identified and their possible functions were predicted. To analyze functions of the bZIP genes, 11 FfbZIPs were selected according to different motifs they contained and were knocked out by genetic recombination. Results of the characteristic studies revealed that these FfbZIPs were involved in oxygen stress, osmotic stress, cell wall selection pressure, cellulose utilization, cell wall penetration, and pathogenicity. In conclusion, this study enhanced understandings of the evolution and regulatory mechanism of the FfbZIPs in fungal growth, abiotic/biotic stress resistance, and pathogenicity, which could be the reference for other fungal bZIP studies.
Keywords: Fusarium fujikuroi; bZIP TF; bakanae disease; functional analysis; phylogenetic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Profiling of bZIP Transcription Factors and FocbZIP11's Impact on Fusarium TR4 Pathogenicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 9;26(4):1452. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041452. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003918 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and analysis of the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor gene family in Ustilaginoidea virens.Genome. 2017 Dec;60(12):1051-1059. doi: 10.1139/gen-2017-0089. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Genome. 2017. PMID: 28841402
-
Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice.Plant Physiol. 2008 Feb;146(2):333-50. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.112821. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18065552 Free PMC article.
-
The puzzle of bakanae disease through interactions between Fusarium fujikuroi and rice.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2017 Jun 1;9(2):333-344. doi: 10.2741/e806. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2017. PMID: 28410155 Review.
-
Abscisic-acid-dependent basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors in plant abiotic stress.Protoplasma. 2017 Jan;254(1):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s00709-015-0920-4. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Protoplasma. 2017. PMID: 26669319 Review.
Cited by
-
The basic leucine zipper domain (bZIP) transcription factor BbYap1 promotes evasion of host humoral immunity and regulates lipid homeostasis contributing to fungal virulence in Beauveria bassiana.mSphere. 2024 Jul 30;9(7):e0035124. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00351-24. Epub 2024 Jun 27. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38926907 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Profiling of bZIP Transcription Factors and FocbZIP11's Impact on Fusarium TR4 Pathogenicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 9;26(4):1452. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041452. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003918 Free PMC article.
-
Phase separation of a master transcription factor targeted by a natural compound regulates fungal ergosterol homeostasis.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Jun 12. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2899-1. Online ahead of print. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40514608
-
Early and Late Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Responses of Rhododendron 'Xiaotaohong' Petals to Infection with Alternaria sp.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 11;24(16):12695. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612695. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628875 Free PMC article.
-
The Identification, Characterization, and Functional Analysis of the Sugar Transporter Gene Family of the Rice False Smut Pathogen, Villosiclava virens.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):600. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010600. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gupta A., Solanki I., Bashyal B., Singh Y. Bakanae of rice: An emerging disease in Asia. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2015;25:1499–1514.
-
- Wiemann P., Sieber C., Bargen K.V., Studt L., Niehaus E.M., Espino J.J., Huß K., Michielse C.B., Albermann S., Wagner D., et al. Deciphering the cryptic genome: Genome-wide analyses of the rice pathogen Fusarium fujikuroi reveal complex regulation of secondary metabolism and novel metabolites. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003475. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003475. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang J., Qu S., Guo Z., Du X., Du B., Zhang Z. Biological functions of plant bZIP transcription factors. Northwest Bot. 2011;44:1066–1075.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

