Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Oxidative Stress as a Double Agent and Its Biological and Therapeutic Significance
- PMID: 35743162
- PMCID: PMC9224361
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126719
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Oxidative Stress as a Double Agent and Its Biological and Therapeutic Significance
Abstract
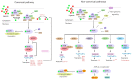
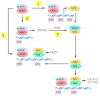
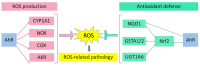
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) has long been implicated in the induction of a battery of genes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. AhR is a ligand-activated transcription factor necessary for the launch of transcriptional responses important in health and disease. In past decades, evidence has accumulated that AhR is associated with the cellular response to oxidative stress, and this property of AhR must be taken into account during investigations into a mechanism of action of xenobiotics that is able to activate AhR or that is susceptible to metabolic activation by enzymes encoded by the genes that are under the control of AhR. In this review, we examine various mechanisms by which AhR takes part in the oxidative-stress response, including antioxidant and prooxidant enzymes and cytochrome P450. We also show that AhR, as a participant in the redox balance and as a modulator of redox signals, is being increasingly studied as a target for a new class of therapeutic compounds and as an explanation for the pathogenesis of some disorders.
Keywords: AhR; Nrf2; antioxidant; aryl hydrocarbon receptor; nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induction of cellular oxidative stress by aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation.Chem Biol Interact. 2002 Sep 20;141(1-2):77-95. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(02)00067-4. Chem Biol Interact. 2002. PMID: 12213386 Review.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor protects lung adenocarcinoma cells against cigarette sidestream smoke particulates-induced oxidative stress.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Mar 15;259(3):293-301. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.01.005. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22273977
-
Coordinate regulation of Phase I and II xenobiotic metabolisms by the Ah receptor and Nrf2.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Jun 15;73(12):1853-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.01.009. Epub 2007 Jan 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17266942 Review.
-
Induction of phase I, II and III drug metabolism/transport by xenobiotics.Arch Pharm Res. 2005 Mar;28(3):249-68. doi: 10.1007/BF02977789. Arch Pharm Res. 2005. PMID: 15832810 Review.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a target of environmental stressors - Implications for pollution mediated stress and inflammatory responses.Redox Biol. 2020 Jul;34:101530. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101530. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32354640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Its Crosstalk: A Chemopreventive Target of Naturally Occurring and Modified Phytochemicals.Molecules. 2024 Sep 10;29(18):4283. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184283. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Indoor Exposure to Airborne Halogenated Flame Retardants TCIPP (Tris(1,3-Dichloro-2-Propyl) Phosphate) and TCEP Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate and Their Hazardous Effects on Biological Systems.Metabolites. 2024 Dec 10;14(12):697. doi: 10.3390/metabo14120697. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39728479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 modulates dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl 126-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity.Environ Res. 2024 Jun 1;250:118492. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118492. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38373550 Free PMC article.
-
Public Health Effects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Exposure Through Air, Water, Soil, and Food in Ghana: Possible Economic Burden.Environ Health Insights. 2025 Jun 19;19:11786302251343767. doi: 10.1177/11786302251343767. eCollection 2025. Environ Health Insights. 2025. PMID: 40548300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Butyrate Produced by Gut Microbiota Regulates Atherosclerosis: A Narrative Review of the Latest Findings.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 14;26(14):6744. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146744. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724991 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pierre S., Chevallier A., Teixeira-Clerc F., Ambolet-Camoit A., Bui L.C., Bats A.S., Fournet J.C., Fernandez-Salguero P., Aggerbeck M., Lotersztajn S., et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent induction of liver fibrosis by dioxin. Toxicol. Sci. 2014;137:114–124. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft236. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

