CircDCLRE1C Regulated Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Regulating miR-214b-3p/STAT3 Pathway in Macrophages
- PMID: 35743265
- PMCID: PMC9224735
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126822
CircDCLRE1C Regulated Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Regulating miR-214b-3p/STAT3 Pathway in Macrophages
Abstract
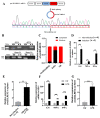
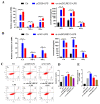
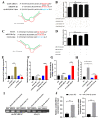
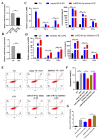
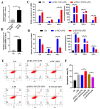
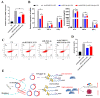
The immune cell inflammation response is closely related to the occurrence of disease, and much evidence has shown that circular RNAs (circRNAs) play vital roles in the occurrence of disease. However, the biological function and regulatory mechanisms of circRNAs in the immune cell inflammation response remain poorly understood. In this study, we constructed an inflammatory model using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated chicken macrophage lines (also known as HD11) to verify the function and mechanism of the novel circDCLRE1C (ID: gga_circ_0001674), which was significantly upregulated in spleen tissues infected by coccidia and the macrophage cells exposed to LPS. The results showed that circDCLRE1C aggravated LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis in HD11 cells. Systemically, circDCLRE1C acted as a sponge for miR-214b-3p binding sites thereby regulating the expression of STAT3. The overexpression of miR-214b-3p rescued the pro-inflammatory effect of circDCLRE1C in HD11 cells stimulated with LPS, and rescued the high expression of STAT3. In conclusion, our study showed that circDCLRE1C could aggravate LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis through competitive adsorption of miR-214b-3p, thereby increasing the expression of STAT3.
Keywords: STAT3; apoptosis; circular RNA; inflammation; macrophage; miR-214b-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circ_0038467 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury in human bronchial epithelial cells through sponging miR-338-3p.Thorac Cancer. 2020 May;11(5):1297-1308. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13397. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32181994 Free PMC article.
-
CircNFIC Balances Inflammation and Apoptosis by Sponging miR-30e-3p and Regulating DENND1B Expression.Genes (Basel). 2021 Nov 19;12(11):1829. doi: 10.3390/genes12111829. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828435 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of circ_0026579 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (bacterial origin)-induced inflammatory injury in bronchial epithelium cells by targeting miR-338-3p/TBL1XR1 axis.Transpl Immunol. 2022 Oct;74:101635. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2022.101635. Epub 2022 May 27. Transpl Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35636669
-
Circ_0114427 promotes LPS-induced septic acute kidney injury by modulating miR-495-3p/TRAF6 through the NF-κB pathway.Autoimmunity. 2022 Feb;55(1):52-64. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1995861. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Autoimmunity. 2022. PMID: 34730059
-
Knockdown of circ_0038467 alleviates lipopolysaccharides-induced 16HBE cell injury by regulating the miR-545-3p/TRAF1 axis in neonatal pneumonia.Microb Pathog. 2022 Dec;173(Pt A):105819. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105819. Epub 2022 Oct 8. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36216207
Cited by
-
Effects of maternal Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide exposure on offspring: insights from lncRNA analysis in laying hens.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104599. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104599. Epub 2024 Nov 30. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39657467 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of circular RNAs on the regulation of production traits in chicken.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104612. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104612. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39647355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
circRNA/TLR interaction: key players in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 6. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04221-9. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40328911 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31761143014/the Natural Scientific Foundation of China
- 2019BT02N630/Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Province
- 202103000084/Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou
- 2021YFD1300100/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2020B1212060060/the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

