Olfactory Training in Post-COVID-19 Persistent Olfactory Disorders: Value Normalization for Threshold but Not Identification
- PMID: 35743346
- PMCID: PMC9224948
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11123275
Olfactory Training in Post-COVID-19 Persistent Olfactory Disorders: Value Normalization for Threshold but Not Identification
Abstract
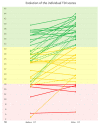
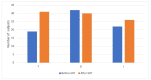
(1) Background: Persistent post-viral olfactory disorders (PPVOD) are estimated at 30% of patients one year after COVID-19 infection. No treatment is, to date, significantly effective on PPVOD with the exception of olfactory training (OT). The main objective of this work was to evaluate OT efficiency on post-COVID-19 PPVOD. (2) Methods: Consecutive patients consulting to the ENT department with post-COVID-19 PPVOD were included after completing clinical examination, the complete Sniffin’ Stick Test (TDI), the short version of the Questionnaire of olfactory disorders and the SF-36. Patients were trained to practice a self-olfactory training with a dedicated olfactory training kit twice a day for 6 months before returning to undergo the same assessments. (3) Results: Forty-three patients were included and performed 3.5 months of OT in average. We observed a significant TDI score improvement, increasing from 24.7 (±8.9) before the OT to 30.9 (±9.8) (p < 0.001). Based on normative data, a significant increase in the number of normosmic participants was observed only for the threshold values (p < 0.001). Specific and general olfaction-related quality of life improved after the OT. (4) Conclusions: Olfactory function appeared to improve only in peripheral aspects of post-COVID-19 PPVOD after OT. Future controlled studies must be performed to confirm the OT role and justify new therapeutic strategies that may focus on the central aspects of post-COVID-19 PPVOD.
Keywords: COVID-19; olfaction disorders; olfactory training; parosmia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Riestra-Ayora J., Yanes-Diaz J., Esteban-Sanchez J., Vaduva C., Molina-Quiros C., Larran-Jimenez A., Martin-Sanz E. Long-Term Follow-up of Olfactory and Gustatory Dysfunction in COVID-19: 6 Months Case—Control Study of Health Workers. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021;278:4831–4837. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06764-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boscolo-Rizzo P., Guida F., Polesel J., Marcuzzo A.V., Antonucci P., Capriotti V., Sacchet E., Cragnolini F., D’Alessandro A., Zanelli E., et al. Self-Reported Smell and Taste Recovery in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: A One-Year Prospective Study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2022;279:515–520. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06839-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lechien J.R., Chiesa-Estomba C.M., Beckers E., Mustin V., Ducarme M., Journe F., Marchant A., Jouffe L., Barillari M.R., Cammaroto G., et al. Prevalence and 6-Month Recovery of Olfactory Dysfunction: A Multicentre Study of 1363 COVID-19 Patients. J. Intern. Med. 2021;290:451–461. doi: 10.1111/joim.13209. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

