Implication of Lipids in Calcified Aortic Valve Pathogenesis: Why Did Statins Fail?
- PMID: 35743402
- PMCID: PMC9225514
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11123331
Implication of Lipids in Calcified Aortic Valve Pathogenesis: Why Did Statins Fail?
Abstract
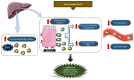
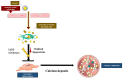
Calcific Aortic Valve Disease (CAVD) is a fibrocalcific disease. Lipoproteins and oxidized phospholipids play a substantial role in CAVD; the level of Lp(a) has been shown to accelerate the progression of valve calcification. Indeed, oxidized phospholipids carried by Lp(a) into the aortic valve stimulate endothelial dysfunction and promote inflammation. Inflammation and growth factors actively promote the synthesis of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and trigger an osteogenic program. The accumulation of ECM proteins promotes lipid adhesion to valve tissue, which could initiate the osteogenic program in interstitial valve cells. Statin treatment has been shown to have the ability to diminish the death rate in subjects with atherosclerotic impediments by decreasing the serum LDL cholesterol levels. However, the use of HMG-CoA inhibitors (statins) as cholesterol-lowering therapy did not significantly reduce the progression or the severity of aortic valve calcification. However, new clinical trials targeting Lp(a) or PCSK9 are showing promising results in reducing the severity of aortic stenosis. In this review, we discuss the implication of lipids in aortic valve calcification and the current findings on the effect of lipid-lowering therapy in aortic stenosis.
Keywords: Lp(a); PCSK9; aortic valve; lipids; statins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipoprotein(a), a Lethal Player in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 27;10:812368. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.812368. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35155427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COX-2 Is Downregulated in Human Stenotic Aortic Valves and Its Inhibition Promotes Dystrophic Calcification.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 24;21(23):8917. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238917. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33255450 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a): Its Association with Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis, the Emerging RNA-Related Treatments and the Hope for a New Era in "Treating" Aortic Valve Calcification.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Feb 23;10(3):96. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10030096. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 36975859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized phospholipids as a unifying theory for lipoprotein(a) and cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019 May;16(5):305-318. doi: 10.1038/s41569-018-0153-2. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30675027 Review.
-
Autotaxin and Lipoprotein Metabolism in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019 Mar 1;6:18. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00018. eCollection 2019. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019. PMID: 30881959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aortic Valve Calcium Score: Applications in Clinical Practice and Scientific Research-A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 11;13(14):4064. doi: 10.3390/jcm13144064. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39064103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Management and Therapy of Severe Aortic Stenosis and Future Perspective.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024 Oct 1;31(10):1353-1364. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV22023. Epub 2024 Aug 8. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024. PMID: 39111841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in the global burden of aortic valve calcification disease in the working-age population from 1992 to 2021.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Aug 12;12:1544273. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1544273. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40873611 Free PMC article.
-
Side- and Disease-Dependent Changes in Human Aortic Valve Cell Population and Transcriptomic Heterogeneity Determined by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing.Genes (Basel). 2024 Dec 19;15(12):1623. doi: 10.3390/genes15121623. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766890 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet membrane-coated alterbrassicene A nanoparticle inhibits calcification of the aortic valve by suppressing phosphorylation P65 NF-κB.Theranostics. 2023 Jun 26;13(11):3781-3793. doi: 10.7150/thno.85323. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37441596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J.H., Chen W.L., Sider K.L., Yip C.Y., Simmons C.A. beta-catenin mediates mechanically regulated, transforming growth factor-beta1-induced myofibroblast differentiation of aortic valve interstitial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011;31:590–597. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.220061. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bouchareb R., Boulanger M.C., Fournier D., Pibarot P., Messaddeq Y., Mathieu P. Mechanical strain induces the production of spheroid mineralized microparticles in the aortic valve through a RhoA/ROCK-dependent mechanism. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2014;67:49–59. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.12.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

