Changes of Acute Kidney Injury Epidemiology during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35743418
- PMCID: PMC9225342
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11123349
Changes of Acute Kidney Injury Epidemiology during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
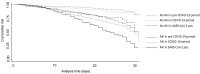
To evaluate the impact of the Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) pandemic on the epidemiology of acute kidney injury (AKI) in hospitalized patients, we performed a retrospective cohort study comparing data of patients hospitalized from January 2016 to December 2019 (pre-COVID-19 period) and from January to December 2020 (COVID-19 period, including both severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-negative and positive patients). AKI was classified by evaluating the kinetics of creatinine levels. A total of 51,681 patients during the pre-COVID-19 period and 10,062 during the COVID-19 period (9026 SARS-CoV-2-negative and 1036 SARS-CoV-2-positive) were analyzed. Patients admitted in the COVID-19 period were significantly older, with a higher prevalence of males. In-hospital AKI incidence was 31.7% during the COVID-19 period (30.5% in SARS-CoV-2-negative patients and 42.2% in SARS-CoV-2-positive ones) as compared to 25.9% during the pre-COVID-19 period (p < 0.0001). In the multivariate analysis, AKI development was independently associated with both SARS-CoV-2 infection and admission period. Moreover, evaluating the pre-admission estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) we found that during the COVID-19 period, there was an increase in AKI stage 2−3 incidence both in patients with pre-admission eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and in those with eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (“de novo” AKI). Similarly, clinical outcomes evaluated as intensive care unit admission, length of hospital stay, and mortality were significantly worse in patients admitted in the COVID-19 period. Additionally, in this case, the mortality was independently correlated with the admission during the COVID-19 period and SARS-CoV-2 infection. In conclusion, we found that during the COVID-19 pandemic, in-hospital AKI epidemiology has changed, not only for patients affected by COVID-19. These modifications underline the necessity to rethink AKI management during health emergencies.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; acute kidney injury; hospitalization; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19 Patients: An Inner City Hospital Experience and Policy Implications.Am J Nephrol. 2020;51(10):786-796. doi: 10.1159/000511160. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Am J Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33011717 Free PMC article.
-
Is the Use of Dialysis Associated With an Increased Risk of Death in COVID-19-Related Acute Kidney Injury?Cureus. 2022 Dec 10;14(12):e32373. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32373. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36632264 Free PMC article.
-
Early reduction of estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) predicts poor outcome in acutely ill hospitalized COVID-19 patients firstly admitted to medical regular wards (eGFR-COV19 study).Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Sep;153:113454. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113454. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36076568 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiles revealed potential kidney injury caused by SARS-CoV-2: a systematic analysis of ACE2 and clinical lessons learned from this discovery.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 21;13(8):10821-10832. doi: 10.18632/aging.202224. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33234728 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Kidney Injury Associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 - One Year Later, What Do We Know So Far?Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021 Nov-Dec;32(6):1543-1551. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.352414. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021. PMID: 35946266 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition patterns of acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Jul 22;17(8):sfae231. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae231. eCollection 2024 Aug. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 39157067 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Injury for Traumatic Mid-Foot Lisfranc Injuries: Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic.Cureus. 2024 Apr 20;16(4):e58644. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58644. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38770506 Free PMC article.
-
Acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients with real-life analysis of incidence and clinical impact in Italian hospitals (the SIN-AKI study).Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 24;15(1):14261. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96236-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40274969 Free PMC article.
-
Global geographic and socioeconomic disparities in COVID-associated acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Glob Health. 2025 Jul 25;15:04166. doi: 10.7189/jogh.15.04166. J Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40709582 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Features and Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study.J Clin Med. 2023 Aug 4;12(15):5127. doi: 10.3390/jcm12155127. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37568528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vena A., Giacobbe D.R., di Biagio A., Mikulska M., Taramasso L., de Maria A., Ball L., Brunetti I., Loconte M., Patroniti N.A., et al. Clinical characteristics, management and in-hospital mortality of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Genoa, Italy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020;26:1537–1544. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.07.049. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hirsch J.S., Ng J.H., Ross D.W., Sharma P., Shah H.H., Barnett R.L., Hazzan A.D., Fishbane S., Jhaveri K.D., on behalf of the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium and the Northwell Nephrology COVID-19 Research Consortium Acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020;98:209–218. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Russo E., Esposito P., Taramasso L., Magnasco L., Saio M., Briano F., Russo C., Dettori S., Vena A., di Biagio A., et al. Kidney disease and all-cause mortality in patients with COVID-19 hospitalized in Genoa, Northern Italy. J. Nephrol. 2021;34:173–183. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00875-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hamilton P., Hanumapura P., Castelino L., Henney R., Parker K., Kumar M., Murphy M., Al-Sayed T., Pinnington S., Felton T., et al. Characteristics and outcomes of hospitalised patients with acute kidney injury and COVID-19. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0241544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241544. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

