Effectiveness and Safety of High-Dose Dual Therapy: Results of the European Registry on the Management of Helicobacterpylori Infection (Hp-EuReg)
- PMID: 35743627
- PMCID: PMC9225562
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11123544
Effectiveness and Safety of High-Dose Dual Therapy: Results of the European Registry on the Management of Helicobacterpylori Infection (Hp-EuReg)
Abstract
Background: Randomized clinical trials and meta-analyses, primarily from Asian countries, have reported good effectiveness with high-dose dual therapy (HDDT) including a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and amoxicillin when prescribed as H. pylori first-line or rescue treatment. However, combining amoxicillin with PPIs in the 1990s in several European countries yielded suboptimal results.
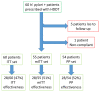
Methods: An international, multicenter, prospective non-interventional Registry (Hp-EuReg) aimed to evaluate the decisions and outcomes of H. pylori management by European gastroenterologists. All infected adult cases treated with HDDT were registered at e-CRF AEG-REDCap platform until June 2021. Sixty patients were prescribed with HDDT (98% compliance), 19 of them received a first-line therapy and 41 a rescue treatment (second- to sixth-line).
Results: Overall HDDT effectiveness was 52% (per-protocol) and 51% (modified intention-to-treat). First-line and rescue treatment lines were equally effective, but the effectiveness was worse when patients had previously received metronidazole, tetracycline, or rifabutin. Adding bismuth to HDDT in rescue treatment did not yield better results. The incidence of adverse events was 30%, diarrhea being the most common (20% of patients); no serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: Although HDDT is safe and has good compliance, it is not a good option in European first-line or rescue H. pylori treatment, even when adding bismuth.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; amoxicillin; effectiveness; eradication; high-dose; registry; rescue treatment; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Gisbert has served as a speaker, consultant, and advisory member for or has received research funding from Mayoly, Allergan, Diasorin, Gebro Pharma, and Richen. Dr. Nyssen has received research funding from Mayoly and Allergan. Dr. Pérez-Aisa has received compensation from Allergan and Mylan for formative actions. Dr. Jonaitis has served as speaker for KRKA. The remaining authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nyssen O.P., Bordin D., Tepes B., Pérez-Aisa Á., Vaira D., Caldas M., Bujanda L., Castro-Fernandez M., Lerang F., Leja M., et al. European Registry on Helicobacter pylori management (Hp-EuReg): Patterns and trends in first-line empirical eradication prescription and outcomes of 5 years and 21,533 patients. Gut. 2021;70:40–54. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321372. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wong B., Xiao S., Hu P., Qian S., Huang N., Li Y., Manan C., Lesmana L., Carpio R., Perez J.Y., et al. Comparison of lansoprazole-based triple and dual therapy for treatment of Helicobacter pylori-related duodenal ulcer: An Asian multicentre double-blind randomized placebo controlled study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000;14:217–224. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00689.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous