Pyogenic Liver Abscess Complicating Acute Cholecystitis: Different Management Options
- PMID: 35744045
- PMCID: PMC9229936
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina58060782
Pyogenic Liver Abscess Complicating Acute Cholecystitis: Different Management Options
Abstract
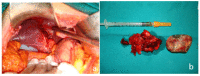
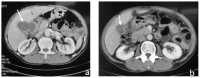
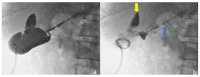
Acute cholecystitis, which is usually associated with gallstones is one of the most common surgical causes of emergency hospital admission and may be further complicated by mural necrosis, perforation and abscess formation. Perforation of the gallbladder is a relatively uncommon complication of acute cholecystitis (0.8-3.2% in recent reviews). The intrahepatic perforation causing a liver abscess is an extremely rare condition, anecdotally reported in the scientific literature, even in the rare types of subacute or acute perforation. Liver abscess caused by gallbladder perforation can be a life-threatening complication with a reported mortality of 5.6%. The treatment of synchronous pyogenic liver abscess and acute cholecystitis may be challenging. We reported three cases of liver abscess due to acute cholecystitis in which different therapeutical approaches were employed. The first case was treated with antibiotics and interval laparoscopic cholecystectomy; the second case was treated with emergency cholecystectomy; and the third case with percutaneous aspiration of the abscess only. The appropriate therapeutical method in these cases depends on the patient's clinical condition, the on-site expertise that is available in the hospital, and the experience of the surgeon.
Keywords: cholecystectomy; cholecystitis; percutaneous; pyogenic liver abscess.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
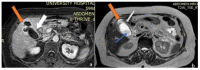
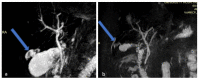
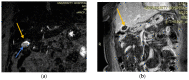
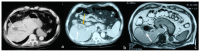

References
-
- Costi R., Le Bian A.Z., Cauchy F., Diop P.S., Carloni A., Catherine L., Smadja C. Synchronous pyogenic liver abscess and acute cholecystitis: How to recognize it and what to do (emergency cholecystostomy followed by delayed laparoscopic cholecystectomy) Surg. Endosc. 2011;26:205–213. doi: 10.1007/s00464-011-1856-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Izadi K., Moser F.G., Haker K., Satey S. Gallstone Liver Abscess Secondary to Gallbladder Perforation. Radiol. Case Rep. 2009;4:280. doi: 10.2484/rcr.v4i2.280. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

