Value of the Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting CPET Performance in Patients with Stable CAD and Recent Elective PCI
- PMID: 35744077
- PMCID: PMC9229341
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina58060814
Value of the Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting CPET Performance in Patients with Stable CAD and Recent Elective PCI
Abstract
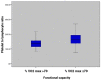
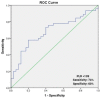
Background and Objectives: Functional capacity (FC) assessed via cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is a novel, independent prognostic marker for patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) are two readily available predictors of systemic inflammation and cardiovascular event risk, which could be used as cost-effective predictors of poor FC. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the utility of NLR and PLR in predicting poor FC in patients with CAD and recent elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Materials and Methods: Our cross-sectional retrospective analysis included 80 patients with stable CAD and recent elective PCI (mean age 55.51 ± 11.83 years, 71.3% male) who were referred to a cardiovascular rehabilitation center from January 2020 to June 2021. All patients underwent clinical examination, cardiopulmonary exercise testing on a cycle ergometer, transthoracic echocardiography and standard blood analysis. Results: Patients were classified according to percent predicted oxygen uptake (% VO2 max) in two groups—poor FC (≤70%, n = 35) and preserved FC (>70%, n = 45). There was no significant difference between groups regarding age, gender ratio, presence of associated comorbidities, left ventricular ejection fraction and NLR. PLR was higher in patients with poor FC (169.8 ± 59.3 vs. 137.4 ± 35.9, p = 0.003). A PLR cut-off point of 139 had 74% sensitivity and 60% specificity in predicting poor FC. After multivariate analysis, PLR remained a significant predictor of poor functional status. Conclusions: Although CPET is the gold standard test for assessing FC prior to cardiovascular rehabilitation, its availability remains limited. PLR, a cheap and simple test, could predict poor FC in patients with stable CAD and recent elective PCI and help prioritize referral for cardiovascular rehabilitation in high-risk patients.
Keywords: cardiopulmonary exercise test; coronary artery disease; functional capacity; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; oxygen uptake; platelet to lymphocyte ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory and Fibrosis Parameters Predicting CPET Performance in Males with Recent Elective PCI for Chronic Coronary Syndrome.Life (Basel). 2025 Mar 21;15(4):510. doi: 10.3390/life15040510. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283065 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Usefulness of the Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting the Long-Term Adverse Events in Patients Who Have Undergone Percutaneous Coronary Intervention with a Drug-Eluting Stent.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133934. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133934. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26207383 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio with coronary artery disease severity in patients undergoing coronary angiography.Kardiol Pol. 2015;73(12):1310-6. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2015.0098. Epub 2015 May 19. Kardiol Pol. 2015. PMID: 25987404
-
Assessment of Inflammatory Hematological Ratios (NLR, PLR, MLR, LMR and Monocyte/HDL-Cholesterol Ratio) in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Particularities in Young Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 21;24(18):14378. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814378. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A practical clinical approach to utilize cardiopulmonary exercise testing in the evaluation and management of coronary artery disease: a primer for cardiologists.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2018 Mar;33(2):168-177. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000494. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29240566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Prognostic Role of Naples Prognostic Score in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease.J Inflamm Res. 2025 May 30;18:6999-7012. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S527868. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40463862 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers and Chest CT Findings as Predictors of Acute Limb Ischemia Risk, Intensive Care Unit Admission, and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 30;12(10):2379. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102379. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292068 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in neutrophil-lymphocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratios before and after percutaneous coronary intervention and their impact on the prognosis of patients with acute coronary syndrome.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2023 Jul 4;78:100221. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2023.100221. eCollection 2023. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2023. PMID: 37413773 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Carotid Plaque Features and Inflammatory Biomarkers as Predictors of Restenosis and Mortality Following Carotid Endarterectomy.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 26;19(21):13934. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192113934. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36360814 Free PMC article.
-
High Baseline Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Could Serve as a Biomarker for Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Blockers and Their Discontinuation in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;16(3):379. doi: 10.3390/ph16030379. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nowbar A.N., Howard J.P., Finegold J.A., Asaria P., Francis D.P. 2014 Global Geographic Analysis of Mortality from Ischaemic Heart Disease by Country, Age and Income: Statistics from World Health Organisation and United Nations. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014;174:293–298. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.04.096. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ambrosetti M., Abreu A., Corrà U., Davos C.H., Hansen D., Frederix I., Iliou M.C., Pedretti R.F., Schmid J.-P., Vigorito C., et al. Secondary Prevention through Comprehensive Cardiovascular Rehabilitation: From Knowledge to Implementation. 2020 Update. A Position Paper from the Secondary Prevention and Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020;28:460–495. doi: 10.1177/2047487320913379. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

