The Mechanism of Dynamic Interaction between Doxorubicin and Calf Thymus DNA at the Single-Molecule Level Based on Confocal Raman Spectroscopy
- PMID: 35744554
- PMCID: PMC9228395
- DOI: 10.3390/mi13060940
The Mechanism of Dynamic Interaction between Doxorubicin and Calf Thymus DNA at the Single-Molecule Level Based on Confocal Raman Spectroscopy
Abstract
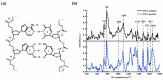
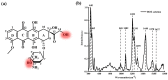
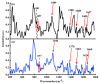
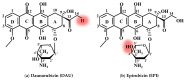
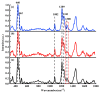
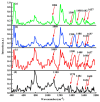
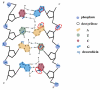
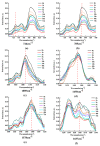
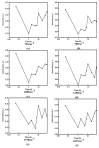
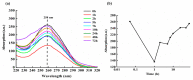
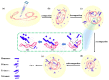
It is of great fundamental significance and practical application to understand the binding sites and dynamic process of the interaction between doxorubicin (DOX) and DNA molecules. Based on the Confocal Raman spectroscopy, the interaction between DOX and calf thymus DNA has been systemically investigated, and some meaningful findings have been found. DOX molecules can not only interact with all four bases of DNA molecules, i.e., adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, and phosphate, but also affect the DNA conformation. Meanwhile, the binding site of DOX and its derivatives such as daunorubicin and epirubicin is certain. Furthermore, the interaction between DOX and DNA molecules is a dynamic process since the intensities of each characteristic peaks of the base, e.g., adenine, cytosine, and phosphate, are all regularly changed with the interaction time. Finally, a dynamic mechanism model of the interaction between DOX and DNA molecules is proposed; that is, there are two kinds of interaction between DOX and DNA molecules: DOX-DNA acts to form a complex, and DOX-DOX acts to form a multimer. The two effects are competitive, as the former compresses DNA molecules, and the latter decompresses these DNA molecules. This work is helpful for accurately understanding and developing new drugs and pathways to improve and treat DOX-induced cytotoxicity and cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: Confocal Raman spectroscopy; binding site; calf thymus DNA; doxorubicin; dynamic process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest relevant to this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects and competitive relationships between DOC and DOX as acting on DNA molecules: Studied with confocal Raman spectroscopy and molecular docking technology.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 23;10(9):e30233. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30233. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38707315 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the Effects and Competitive Mechanisms of YOYO-1 on the Binding Characteristics of DOX and DNA Molecules Based on Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking Techniques.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 28;25(7):3804. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073804. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612614 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy for multiple-site equilibrium binding: a case of doxorubicin-DNA interaction.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2019 Jan 21;21(3):1572-1577. doi: 10.1039/c8cp06752j. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2019. PMID: 30620015
-
Potential targets for intervention against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity based on genetic studies: a systematic review of the literature.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020 Jan;138:88-98. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.11.150. Epub 2019 Nov 18. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31751567
-
The Protective Effect of Natural Compounds on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase Inhibition.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 3;74(3):351-359. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgab109. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34562089 Review.
Cited by
-
UV-Resonance Raman Spectra of Systems in Complex Environments: A Multiscale Modeling Applied to Doxorubicin Intercalated into DNA.J Chem Inf Model. 2023 Feb 27;63(4):1208-1217. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01495. Epub 2023 Feb 6. J Chem Inf Model. 2023. PMID: 36745496 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects and competitive relationships between DOC and DOX as acting on DNA molecules: Studied with confocal Raman spectroscopy and molecular docking technology.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 23;10(9):e30233. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30233. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38707315 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional molecular hybrid for targeted colorectal cancer cells: Integrating doxorubicin, AS1411 aptamer, and T9/U4 ASO.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 13;20(2):e0317559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317559. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39946362 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Doxorubicin Embedded into Phospholipid Nanoparticles and Targeted Peptide-Modified Phospholipid Nanoparticles with DNA.Molecules. 2023 Jul 10;28(14):5317. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145317. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513191 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the Interaction between Bendamustine and DNA Molecule with SERS Based on AuNPs/ZnCl2/NpAA Solid-State Substrate.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 31;24(17):13517. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713517. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolat G. Investigation of poly (CTAB-MWCNTs) composite based electrochemical DNA biosensor and interaction study with anticancer drug Irinotecan. Microchem. J. 2020;159:105426. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2020.105426. - DOI
-
- Joksimović N., Petronijević J., Milović E., Janković N., Baskić D., Popović S., Todorović D., Matić S., Vranes M., Tot A. Synthesis, characterization, antitumor potential, BSA and DNA binding properties, and molecular docking study of some novel 3-hydroxy-3-pyrrolin-2-ones. Med. Chem. 2021;18:337–352. doi: 10.2174/1573406417666210803094127. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

