Design and Development of a Smart IoT-Based Robotic Solution for Wrist Rehabilitation
- PMID: 35744587
- PMCID: PMC9227621
- DOI: 10.3390/mi13060973
Design and Development of a Smart IoT-Based Robotic Solution for Wrist Rehabilitation
Abstract
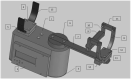
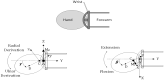
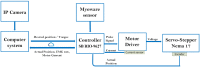
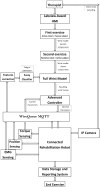
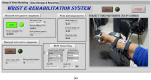
In this study, we present an IoT-based robot for wrist rehabilitation with a new protocol for determining the state of injured muscles as well as providing dynamic model parameters. In this model, the torque produced by the robot and the torque provided by the patient are determined and updated taking into consideration the constraints of fatigue. Indeed, in the proposed control architecture based on the EMG signal extraction, a fuzzy classifier was designed and implemented to estimate muscle fatigue. Based on this estimation, the patient's torque is updated during the rehabilitation session. The first step of this protocol consists of calculating the subject-related parameters. This concerns axis offset, inertial parameters, passive stiffness, and passive damping. The second step is to determine the remaining component of the wrist model, including the interaction torque. The subject must perform the desired movements providing the torque necessary to move the robot in the desired direction. In this case, the robot applies a resistive torque to calculate the torque produced by the patient. After that, the protocol considers the patient and the robot as active and all exercises are performed accordingly. The developed robotics-based solution, including the proposed protocol, was tested on three subjects and showed promising results.
Keywords: human robot interaction; robotic rehabilitation; wrist modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Development of a New Control System for a Rehabilitation Robot Using Electrical Impedance Tomography and Artificial Intelligence.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Sep 11;8(5):420. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8050420. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754171 Free PMC article.
-
A New Wrist-Forearm Rehabilitation Protocol Integrating Human Biomechanics and SVM-Based Machine Learning for Muscle Fatigue Estimation.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Feb 6;10(2):219. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10020219. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829713 Free PMC article.
-
Myoelectrically controlled wrist robot for stroke rehabilitation.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2013 Jun 10;10:52. doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-10-52. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2013. PMID: 23758925 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Research on assist-as-needed control strategy of wrist function-rehabilitation robot].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 25;37(1):129-135. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201902023. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32096386 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Human-robot coupling dynamic modeling and analysis for upper limb rehabilitation robots.Technol Health Care. 2021;29(4):709-723. doi: 10.3233/THC-202424. Technol Health Care. 2021. PMID: 33386832
Cited by
-
Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation Architecture Supported by a Distributed Data Acquisition System.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 6;22(23):9532. doi: 10.3390/s22239532. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36502234 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a New Control System for a Rehabilitation Robot Using Electrical Impedance Tomography and Artificial Intelligence.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Sep 11;8(5):420. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8050420. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754171 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Density sEMG-Based Pattern Recognition of Unrelated Movements Rejection for Wrist Joint Rehabilitation.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;14(3):555. doi: 10.3390/mi14030555. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984962 Free PMC article.
-
Microrobots in Micromachines.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Jul 29;13(8):1207. doi: 10.3390/mi13081207. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36014128 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid EMG-NMES control for real-time muscle fatigue reduction in bionic hands.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05829-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GWorld Health Organization Stroke, Cerebrovascular Accident. [(accessed on 3 August 2020)]. Available online: http://www.emro.who.int/health-topics/strokecerebrovascularaccident/inde....
-
- Samaee S., Kobravi H.R. Predicting the occurrence of wrist tremor based on electromyography using a hidden Markov model and entropy based learning algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2019;57:101739. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101739. - DOI
-
- Moghaddam M.M., Moshaii A.A., Niestanak V.D. Fuzzy sliding mode control of a wearable rehabilitation robot for wrist and finger. [(accessed on 1 June 2022)];Ind. Robot. 2019 46 Available online: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IR-05-2019-0110/full.... - DOI
-
- Tran V.D., Dario P., Mazzoleni S., Posteraro F. Wrist robot-assisted rehabilitation treatment in subacute and chronic stroke patients: From distal-to-proximal motor recovery. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018;26:1889–1896. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

