Targeting the Holy Triangle of Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Antibiotic Resistance in Pathogenic Bacteria
- PMID: 35744757
- PMCID: PMC9228545
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10061239
Targeting the Holy Triangle of Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Antibiotic Resistance in Pathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
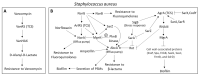
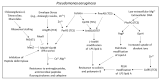
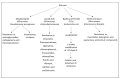
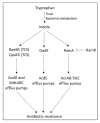
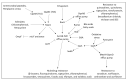
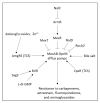
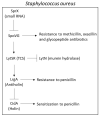
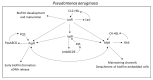
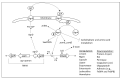
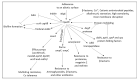
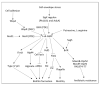
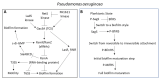
Chronic and recurrent bacterial infections are frequently associated with the formation of biofilms on biotic or abiotic materials that are composed of mono- or multi-species cultures of bacteria/fungi embedded in an extracellular matrix produced by the microorganisms. Biofilm formation is, among others, regulated by quorum sensing (QS) which is an interbacterial communication system usually composed of two-component systems (TCSs) of secreted autoinducer compounds that activate signal transduction pathways through interaction with their respective receptors. Embedded in the biofilms, the bacteria are protected from environmental stress stimuli, and they often show reduced responses to antibiotics, making it difficult to eradicate the bacterial infection. Besides reduced penetration of antibiotics through the intricate structure of the biofilms, the sessile biofilm-embedded bacteria show reduced metabolic activity making them intrinsically less sensitive to antibiotics. Moreover, they frequently express elevated levels of efflux pumps that extrude antibiotics, thereby reducing their intracellular levels. Some efflux pumps are involved in the secretion of QS compounds and biofilm-related materials, besides being important for removing toxic substances from the bacteria. Some efflux pump inhibitors (EPIs) have been shown to both prevent biofilm formation and sensitize the bacteria to antibiotics, suggesting a relationship between these processes. Additionally, QS inhibitors or quenchers may affect antibiotic susceptibility. Thus, targeting elements that regulate QS and biofilm formation might be a promising approach to combat antibiotic-resistant biofilm-related bacterial infections.
Keywords: ESKAPE bacteria; antibiotic resistance; antibiotic sensitization; biofilm; biofilm inhibitors; efflux pump inhibitors; quorum sensing; quorum sensing inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

