Protective Effects of Liquiritigenin against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity via NRF2/SIRT3-Mediated Improvement of Mitochondrial Function
- PMID: 35744945
- PMCID: PMC9231399
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27123823
Protective Effects of Liquiritigenin against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity via NRF2/SIRT3-Mediated Improvement of Mitochondrial Function
Abstract
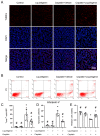
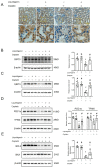
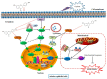
Acute kidney injury (AKI) induced by cisplatin (CP), a first-line anticancer drug for chemotherapy, is common. To date, there is an urgent need to find effective treatments to reduce the nephrotoxicity caused by CP. Meanwhile, the restoration of mitochondrial dysfunction shows potential to be used as an adjunct to conventional therapeutic strategies. This study found that liquiritigenin can ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction and acute kidney injury induced by CP in mice. The intraperitoneal injection of 15 mg/kg body weight liquiritigenin for 2 days markedly protected against CP-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, restored renal tubule and mitochondrial morphology, decreased blood Scr and BUN levels, and decreased cell apoptosis. Furthermore, the elevated expression of SIRT3 induced by liquiritigenin, which can be upregulated by NRF2, was confirmed in vivo and in vitro. The underlying protective mechanisms of liquiritigenin in CP-induced nephrotoxicity were then investigated. Molecular docking results showed that liquiritigenin has potent binding activities to KEAP1, GSK-3β and HRD1. Further results showed that liquiritigenin induced the nuclear translocation of NRF2 and increased the levels of mitochondrial bioenergetics-related protein such as PGC-1α, and TFAM, which are related to NRF2 activity and mitochondrial biogenesis. In addition, liquiritigenin was found to possibly reverse the decrease in BCL2/BAX ratio induced by CP in live cultured renal tubule epithelial cells. Collectively, these results indicated that liquiritigenin could be used as a potential nephroprotective agent to protect against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in a NRF2-dependent manner by improving mitochondria function.
Keywords: NRF2; SIRT3; cisplatin; liquiritigenin; mitochondrial biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bioactive peptide apelin rescues acute kidney injury by protecting the function of renal tubular mitochondria.Amino Acids. 2021 Aug;53(8):1229-1240. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03028-1. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 34254213
-
MicroRNA-140-5p attenuated oxidative stress in Cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by activating Nrf2/ARE pathway through a Keap1-independent mechanism.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Nov 15;360(2):292-302. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28928081
-
Matrine alleviates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation via SIRT3/OPA1 pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jul;26(13):3702-3715. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17398. Epub 2022 Jun 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35650472 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 for protection against oxidant generation and mitochondrial damage in cardiac injury.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Feb 1;179:133-143. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.12.001. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 34921930 Review.
-
Role of curcumin in the treatment of acute kidney injury: research challenges and opportunities.Phytomedicine. 2022 Sep;104:154306. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154306. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35809376 Review.
Cited by
-
Nephroprotective effects of substances of medicine food homology and traditional Chinese medicine phytochemicals against acute kidney injury.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 19;16:1539886. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1539886. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40046749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polygonatum sibiricum component liquiritigenin restrains breast cancer cell invasion and migration by inhibiting HSP90 and chaperone-mediated autophagy.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 1;28(4):379-387. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2024.28.4.379. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38926844 Free PMC article.
-
Acute kidney injury: pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions.Mol Biomed. 2025 Sep 5;6(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s43556-025-00293-4. Mol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40911105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asiaticoside Mitigates Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Modulating TRIM27 Stability and Activating PGC-1α/Nrf2 Signaling.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.1007/s12010-025-05288-z. Online ahead of print. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40668528
-
Harnessing mitochondrial biogenesis to combat acute kidney injury: Current insights and futuredirections.Genes Dis. 2025 Apr 15;12(6):101645. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101645. eCollection 2025 Nov. Genes Dis. 2025. PMID: 40821125 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

