Uncovering the Molecular Basis for the Better Gefitinib Sensitivity of EGFR with Complex Mutations over Single Rare Mutation: Insights from Molecular Simulations
- PMID: 35744964
- PMCID: PMC9230809
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27123844
Uncovering the Molecular Basis for the Better Gefitinib Sensitivity of EGFR with Complex Mutations over Single Rare Mutation: Insights from Molecular Simulations
Abstract
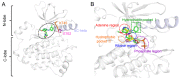
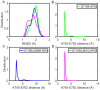
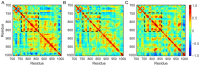
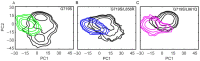
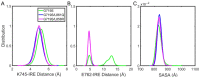
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is an intensively focused target for anti-tumor compounds used in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) therapy. Compared to the classical activating mutations, there are still many uncommon EGFR mutations associated with poorer responses to EGFR inhibitors. A detailed understanding of the molecular basis for multiple EGFR mutants exhibiting diverse responses to inhibitors is of critical importance for related drug development. Herein, we explored the molecular determinants contributing to the distinct responses of EGFR with a single rare mutation (G719S) or combined mutations (G719S/L858R and G719S/l861Q) to Gefitinib (IRE). Our results indicated that interactions, formed within the tetrad of residues S768 (in the αC-helix), D770 (in the αC-β4 loop), Y827 (in the αE-helix), and R831 (in the catalytic loop), play an important role in the stability of αC-helix and the maintenance of K745-E762 salt bridge in the absence of IRE, which are weakened in the EGFRG719S system and enhanced in the EGFRG719S/L858R system upon IRE binding. Besides, the introduced hydrogen bonds by the co-occurring mutation partner also contribute to the stability of αC-helix. The work done for inhibitor dissociation suggests that IRE exhibits a stronger binding affinity to EGFRG719S/L858R mutant. Together, these findings provide a deeper understanding of minor mutations, which is essential for drug development targeting EGFR with less common mutations.
Keywords: EGFR complex mutations; EGFR rare mutants; Gefitinib (IRE); molecular dynamics simulation; steered molecular dynamics simulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for the altered drug sensitivities of non-small cell lung cancer-associated mutants of human epidermal growth factor receptor.Oncogene. 2013 Jan 3;32(1):27-38. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.21. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22349823
-
Prediction of sensitivity to gefitinib/erlotinib for EGFR mutations in NSCLC based on structural interaction fingerprints and multilinear principal component analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Mar 7;19(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2093-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29514601 Free PMC article.
-
Structural signature of the G719S-T790M double mutation in the EGFR kinase domain and its response to inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2014 Aug 5;4:5868. doi: 10.1038/srep05868. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25091415 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal management of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor mutations.Drugs. 2011 Jan 1;71(1):79-88. doi: 10.2165/11587560-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21175241 Review.
-
The use of first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with NSCLC and somatic EGFR mutations.Lung Cancer. 2008 Jun;60 Suppl 2:S19-22. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5002(08)70101-6. Lung Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18513580 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical and structural basis for differential inhibitor sensitivity of EGFR with distinct exon 19 mutations.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 10;13(1):6791. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34398-z. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36357385 Free PMC article.
-
A L833V/H835L EGFR variant lung adenocarcinoma with skin metastasis: A case report and literature review.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 5;8(12):e12080. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12080. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36531621 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches.Open Life Sci. 2023 Nov 27;18(1):20220768. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0768. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 38035047 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery: A Bibliometric Analysis and Literature Review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(14):1353-1367. doi: 10.2174/0113895575271267231123160503. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38243944 Review.
-
Successful treatment of lung adenocarcinoma complicated with a rare compound EGFR mutation L833V/H835L using aumolertinib: a case report and literature review.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 29;14:1257592. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1257592. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37719840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Day K.C., Lorenzatti Hiles G., Kozminsky M., Dawsey S.J., Paul A., Broses L.J., Shah R., Kunja L.P., Hall C., Palanisamy N., et al. HER2 and EGFR Overexpression Support Metastatic Progression of Prostate Cancer to Bone. Cancer Res. 2017;77:74–85. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1656. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arcila M.E., Nafa K., Chaft J.E., Rekhtman N., Lau C., Reva B.A., Zakowski M.F., Kris M.G., Ladanyi M. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013;12:220–229. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jackman D.M., Yeap B.Y., Sequist L.V., Lindeman N., Holmes A.J., Joshi V.A., Bell D.W., Huberman M.S., Halmos B., Rabin M.S., et al. Exon 19 deletion mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor are associated with prolonged survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:3908–3914. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0462. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

