The Role of Saponins in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
- PMID: 35745079
- PMCID: PMC9227328
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27123956
The Role of Saponins in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
Neuropathic pain is a chronic pain caused by tissue injury or disease involving the somatosensory nervous system, which seriously affects the patient's body function and quality of life. At present, most clinical medications for the treatment of neuropathic pain, including antidepressants, antiepileptic drugs, or analgesics, often have limited efficacy and non-negligible side effects. As a bioactive and therapeutic component extracted from Chinese herbal medicine, the role of the effective compounds in the prevention and treatment of neuropathic pain have gradually become a research focus to explore new analgesics. Notably, saponins have shown analgesic effects in a large number of animal models. In this review, we summarized the most updated information of saponins, related to their analgesic effects in neuropathic pain, and the recent progress on the research of therapeutic targets and the potential mechanisms. Furthermore, we put up with some perspectives on future investigation to reveal the precise role of saponins in neuropathic pain.
Keywords: chemical structure; mechanism; neuropathic pain; saponins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
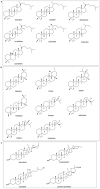
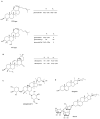
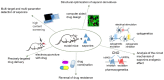
References
-
- Raja S.N., Carr D.B., Cohen M., Finnerup N.B., Flor H., Gibson S., Keefe F.J., Mogil J.S., Ringkamp M., Sluka K.A., et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: Concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain. 2020;161:1976–1982. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001939. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

