Preparation of Cotton Linters' Aerogel-Based C/NiFe2O4 Photocatalyst for Efficient Degradation of Methylene Blue
- PMID: 35745360
- PMCID: PMC9230095
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12122021
Preparation of Cotton Linters' Aerogel-Based C/NiFe2O4 Photocatalyst for Efficient Degradation of Methylene Blue
Abstract
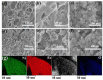
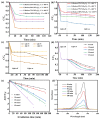
At present, the research focus has been aimed at the pursuit of the design and synthesis of catalysts for effective photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater, and further exploration of novel materials of the photodegradation catalyst. In this paper, the Sol-gel route after thermal treatment was used to produce NiFe2O4 carbon aerogel (NiFe2O4-CA) nanocomposites with cotton linter cellulose as the precursor of aerogel, by co-precipitating iron and nickel salts onto its substrate. The structure and composition of these materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), Raman spectra, high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (HR-SEM), high-resolution scanning electron microscope mapping (SEM-mapping), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET)'s surface area. The magnetic properties of the material were analyzed by a vibrating-sample magnetometer (VSM). Moreover, diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and photo-luminescence spectroscopy (PL) characterized the photoelectric properties of this cellulose-aerogels-based NiFe2O4-CA. Methylene blue (MB) acted as the simulated pollutant, and the photocatalytic activity of NiFe2O4-CA nanocomposites under visible light was evaluated by adjusting H2O2 content and the pH value. The results showed that the optical absorption range of nickel ferrite was broadened by doping cellulose-aerogels-based carbon, which exerted more positive effects on photocatalytic reactions. This is because the doping of this aerogel carbon promoted a more uniform distribution of NiFe2O4 particles. Given the Methylene blue (MB) degradation reaction conformed to the first-order kinetic equation, the NiFe2O4-CA nanocomposites conducted excellent catalytic activity by maintaining almost 99% of the removal of MB (60 mg/L) within 180 min and upheld excellent stability over four consecutive cycles. This study indicated that NiFe2O4-CA nanocomposites reserved the potential as a future effective treatment of dye wastewater.
Keywords: NiFe2O4; carbon aerogel; cellulose; magnetism; photo-Fenton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Fabrication and photocatalytic property of magnetic SrTiO3/NiFe2O4 heterojunction nanocomposites.RSC Adv. 2018 Jan 31;8(10):5441-5450. doi: 10.1039/c7ra12393k. eCollection 2018 Jan 29. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35542406 Free PMC article.
-
Solar driven highly efficient photocatalyst based on Dy2O3 nanorods deposited on reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for methylene blue dye degradation.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Oct;31(50):60260-60278. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-35226-1. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39377909
-
Investigation of structural, optical, and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 for efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants through photo fenton reactions.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 30;10(17):e37199. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37199. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39319118 Free PMC article.
-
A magnetically separable plate-like cadmium titanate-copper ferrite nanocomposite with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic degradation performance for organic contaminants.RSC Adv. 2019 May 17;9(27):15615-15628. doi: 10.1039/c9ra01968e. eCollection 2019 May 14. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35514850 Free PMC article.
-
MoS2-based nanocomposites and aerogels for antibiotic pollutants removal from wastewater by photocatalytic degradation process: A review.Chemosphere. 2024 Apr;354:141582. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141582. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Chemosphere. 2024. PMID: 38462179 Review.
Cited by
-
Tetracycline Removal by Hercynite-Biochar from the Co-Pyrolysis of Red Mud-Steel Slag-Sludge.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 28;12(15):2595. doi: 10.3390/nano12152595. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35957024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang B., Chen M., Li D., Xu H., Xia D. Quantitative investigation into the enhancing utilization efficiency of H2O2catalyzed by FeOCl under visible light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020;386:112072. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112072. - DOI
-
- Ren Y., Dong Q., Feng J., Ma J., Wen Q., Zhang M. Magnetic porous ferrospinel NiFe2O4: A novel ozonation catalyst with strong catalytic property for degradation of di-n-butyl phthalate and convenient separation from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;382:90–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2012.05.053. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

