Oral Manifestations of Syphilis: Report of Four Cases
- PMID: 35745466
- PMCID: PMC9231211
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11060612
Oral Manifestations of Syphilis: Report of Four Cases
Abstract
Syphilis is an infectious disease caused by Treponema pallidum. Syphilis can present with an array of oral manifestations at different stages of disease progression. This article reports on four cases of syphilis with oral manifestations diagnosed by oral health professionals. Case 1: 18-year-old female presented with multiple ulcerations and patches involving the hard palate, uvula, retromolar area, and papillary nodules on the tongue. Case 2: 25-year-old male presented with a solitary, exophytic lesion on the anterior tongue. Case 3: 17-year-old female presented with multiple pigmented macules on the palms of hands and soles of feet, as well as multiple exophytic, sessile, soft tissue masses throughout the oral cavity. Case 4: 14-year-old female presented with a solitary, exophytic, verrucous lesion in the incisive papilla area, as well as multiple, coalescing patches involving the soft palate, uvula, and tonsillar areas. All patients were managed by biopsy and serological investigations. Treatment of syphilis was performed at infectious disease clinics with 2.4 million units (MUs) benzathine benzylpenicillin intramuscular (IM) weekly. Oral health professionals need to have knowledge of the oral manifestations of syphilis to ensure that patients are accurately identified and appropriately treated.
Keywords: Treponema pallidum; oral health; oral lesions; sexually transmitted infections; syphilis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
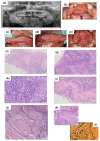

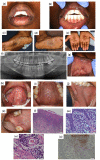

References
-
- Onoya D., Manjengwa P., Nattey C., Kgowedi S., Mbele M., Shumba K., Fox M.P. Incidence and predictors of sexually transmitted infections among adult HIV-positive patients receiving antiretroviral therapy at Themba Lethu HIV clinic in Johannesburg, South Africa. S. Afr. Med. J. 2021;111:80–86. doi: 10.7196/SAMJ.2020.v111i1.14672. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Francis S.C., Mthiyane T.N., Baisley K., Mchunu S.L., Ferguson J.B., Smit T., Crucitti T., Gareta D., Dlamini S., Mutevedzi T., et al. Prevalence of sexually transmitted infections among young people in South Africa: A nested survey in a health and demographic surveillance site. PLoS Med. 2018;15:e1002512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002512. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dobson S., Sanchez P. In: Feigin and Cherry’s Infectious Pediatric Textbook of Diseases. 7th ed. Cherry G., Demmler-Harrison S., Kaplan W., Steinbach P.H., editors. Saunders; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2014. pp. 1761–1782.
-
- Schlossberg D., editor. Clinical Infectious Disease. 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2015. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

