Accurate Mass Identification of an Interfering Water Adduct and Strategies in Development and Validation of an LC-MS/MS Method for Quantification of MPI8, a Potent SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitor, in Rat Plasma in Pharmacokinetic Studies
- PMID: 35745595
- PMCID: PMC9228185
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15060676
Accurate Mass Identification of an Interfering Water Adduct and Strategies in Development and Validation of an LC-MS/MS Method for Quantification of MPI8, a Potent SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitor, in Rat Plasma in Pharmacokinetic Studies
Abstract
MPI8, a peptidyl aldehyde, is a potent antiviral agent against coronavirus. Due to unique tri-peptide bonds and the formyl functional group, the bioassay of MPI8 in plasma was challenged by a strong interference from water MPI8. Using QTOF LC-MS/MS, we identified MPI8•H2O as the major interference form that co-existed with MPI8 in aqueous and biological media. To avoid the resolution of MPI8 and MPI8•H2O observed on reverse phase columns, we found that a Kinetex hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) column provided co-elution of both MPI8 and MPI8•H2O with a good single chromatographic peak and column retention of MPI8 which is suitable for quantification. Thus, a sensitive, specific, and reproducible LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of MPI8 in rat plasma was developed and validated using a triple QUAD LC-MS/MS. The chromatographic separation was achieved on a Kinetex HILIC column with a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min under gradient elution. The calibration curves were linear (r2 > 0.99) over MPI8 concentrations from 0.5−500 ng/mL. The accuracy and precision are within acceptable guidance levels. The mean matrix effect and recovery were 139% and 73%, respectively. No significant degradation of MPI8 occurred under the experimental conditions. The method was successfully applied to a pharmacokinetic study of MPI8 after administration of MPI8 sulfonate in rats.
Keywords: LC-MS/MS; MPI8; MPI8•H2O adduct; SARS-CoV-2; method development and validation; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
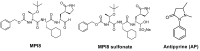






Similar articles
-
A UHPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of JIB-04 in rat plasma: Development, validation and application to pharmacokinetics study.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Nov 30;191:113587. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113587. Epub 2020 Aug 25. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020. PMID: 32892084 Free PMC article.
-
A simple and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for quantification of Bepridil in rat plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic studies.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Aug 5;172:113-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.04.038. Epub 2019 Apr 18. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 31029800
-
Simultaneous determination of 11 alkaloids in rat plasma by LC-ESI-MS/MS and a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of total alkaloids extracted from Naucleaofficinalis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 10;282:114560. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114560. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34454053
-
Development and validation of a HILIC-MS/MS method for quantification of decitabine in human plasma by using lithium adduct detection.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Oct 15;969:117-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.08.012. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25168795
-
Determination of nootkatone in rat plasma by LC-tandem mass spectrometry and its application in a pharmacokinetic study.Biomed Chromatogr. 2021 Dec;35(12):e5197. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5197. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Biomed Chromatogr. 2021. PMID: 34162012
Cited by
-
A systematic exploration of boceprevir-based main protease inhibitors as SARS-CoV-2 antivirals.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Oct 5;240:114596. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114596. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35839690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khandia R., Singhal S., Alqahtani T., Kamal M.A., Nahed A., Nainu F., Desingu P.A., Dhama K. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B. 1.1. 529) variant, salient features, high global health concerns and strategies to counter it amid ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Res. 2022;209:112816. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.112816. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

