Design and Synthesis of a Mitochondria-Targeting Radioprotectant for Promoting Skin Wound Healing Combined with Ionizing Radiation Injury
- PMID: 35745640
- PMCID: PMC9229538
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15060721
Design and Synthesis of a Mitochondria-Targeting Radioprotectant for Promoting Skin Wound Healing Combined with Ionizing Radiation Injury
Abstract
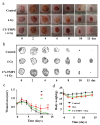
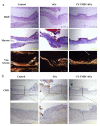
Wound healing is seriously retarded when combined with ionizing radiation injury, because radiation-induced excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) profoundly affect cell growth and wound healing. Mitochondria play vital roles not only as cellular energy factories but also as the main source of endogenous ROS, and in this work a mitochondria-targeting radioprotectant (CY-TMP1) is reported for radiation injury-combined wound repair. It was designed, synthesized and screened out from different conjugates between mitochondria-targeting heptamethine cyanine dyes and a peroxidation inhibitor 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyloxy (TEMPO). CY-TMP1 specifically accumulated in mitochondria, efficiently mitigated mitochondrial ROS and total intracellular ROS induced by 6 Gy of X-ray ionizing irradiation, thereby exhibiting a notable radioprotective effect. The mechanism study further demonstrated that CY-TMP1 protected mitochondria from radiation-induced injury, including maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and ATP generation, thereby reducing the ratio of cell apoptotic death. Particularly, an in vivo experiment showed that CY-TMP1 could effectively accelerate wound closure of mice after 6 Gy of whole-body ionizing radiation. Immunohistochemical staining further indicated that CY-TMP1 may improve wound repair through angiogenesis and re-epithelialization. Therefore, mitochondria-targeting ROS scavengers may present a feasible strategy to conquer refractory wound combined with radiation injury.
Keywords: heptamethine cyanine dye; mitochondrion; radiation protection; wound repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Hay R.J., Johns N.E., Williams H.C., Bolliger I.W., Dellavalle R.P., Margolis D.J., Marks R., Naldi L., Weinstock M.A., Wulf S.K., et al. The global burden of skin disease in 2010: An analysis of the prevalence and impact of skin conditions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014;134:1527–1534. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.446. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bourdais R., Achkar S., Honoré C., Faron M., Cavalcanti A., Auzac G., Ngo C., Haddag-Miliani L., Verret B., Dumont S., et al. Prospective evaluation of intensity-modulated radiotherapy toxicity in extremity soft tissue sarcomas patients: A role for irradiated healthy soft tissue volume? Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021;29:79–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2021.05.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

