Mechanistic Approach of Nano Carriers for Targeted in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Newer Strategy for Novel Drug Delivery System
- PMID: 35745897
- PMCID: PMC9231136
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14122321
Mechanistic Approach of Nano Carriers for Targeted in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Newer Strategy for Novel Drug Delivery System
Abstract
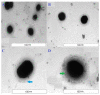
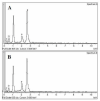
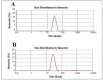
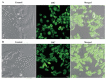
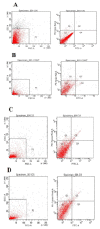
The application of nanomedicine represents an innovative approach for the treatment in the modern field of cancer chemotherapy. In the present research work, tamoxifen citrate loaded nanolipid vesicles were prepared conjugated with phosphoethanolamine as the linker molecule, and the specific antibody was tagged with the linker molecule on the bilayer surface of the vesicles. The main objective of this study is to determine the efficacy and biological behavior of antibody conjugated nanoliposome in breast cancer cell lines. Percentage of drug loading and loading efficiency was done and their results were compared to theoretical drug loading. The average diameter of those vesicles was within the 100 nm range, which is revealed in FESEM and TEM images and their lamellarity was observed in cryo-TEM images. The hydrodynamic diameter was done by particle size analysis and the surface charge was determined by the zeta potential parameter. Predominant cellular uptake was observed for antibody conjugated nanolipid vesicles in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-453 human breast cancer cell lines. A cellular apoptosis assay was conducted by flow cytometer (FACS). All experimental data would be more beneficial for the treatment of breast cancer chemotherapy. Further studies are warranted to investigate the efficacy and safety of antibody conjugated nanolipid vesicles in vivo for breast cancer animal model.
Keywords: breast cancer chemotherapy; cellular apoptosis; nanolipid vesicles; specific antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Development of Linker-Conjugated Nanosize Lipid Vesicles: A Strategy for Cell Selective Treatment in Breast Cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(4):357-72. doi: 10.2174/1568009616666151106120606. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26548758
-
Dual stimuli polysaccharide nanovesicles for conjugated and physically loaded doxorubicin delivery in breast cancer cells.Nanoscale. 2015 Apr 21;7(15):6636-52. doi: 10.1039/c5nr00799b. Nanoscale. 2015. PMID: 25797322
-
Enhancing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Tamoxifen Citrate Loaded Span-Based Nano-Vesicles on Human Breast Adenocarcinoma Cells.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018 May;19(4):1529-1543. doi: 10.1208/s12249-018-0962-y. Epub 2018 Feb 22. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018. PMID: 29470829
-
Antibody-drug nanoparticle induces synergistic treatment efficacies in HER2 positive breast cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 1;11(1):7347. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86762-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33795712 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted nutlin-3a loaded nanoparticles inhibiting p53-MDM2 interaction: novel strategy for breast cancer therapy.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2011 Apr;6(3):489-507. doi: 10.2217/nnm.10.102. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2011. PMID: 21542687
Cited by
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Folic Acid-Functionalized DPLA-co-PEG Nanomicelles for the Targeted Delivery of Letrozole.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023 May 15;6(5):1806-1815. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00041. Epub 2023 Apr 24. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023. PMID: 37093754 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

