Tailoring Natural-Based Oleogels Combining Ethylcellulose and Virgin Coconut Oil
- PMID: 35746048
- PMCID: PMC9230444
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14122473
Tailoring Natural-Based Oleogels Combining Ethylcellulose and Virgin Coconut Oil
Abstract
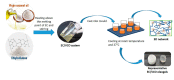
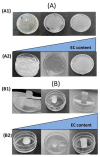
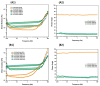
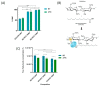
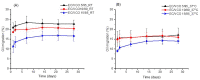
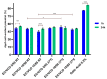
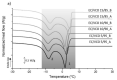
Oleogels are becoming an attractive research field, since they have recently been shown to be feasible for the food and pharmaceutical sectors and provided some insights into the biomedical area. In this work, edible oleogels were tailored through the combination of ethylcellulose (EC), a gelling agent, with virgin coconut oil (VCO), vegetable oil derived from coconut. The influence of the different EC and VCO ratios on the structural, physical, and thermal properties of the oleogels was studied. All EC/VCO-based oleogels presented a stable network with a viscoelastic nature, adequate structural stability, modulable stiffness, high oil-binding capability, antioxidant activity, and good thermal stability, evidencing the EC and VCO's good compatibility.
Keywords: 3D archictectures; ethylcellulose; oleogelation; oleogels; virgin coconut oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and Characterization of Ethylcellulose Oleogels Based on Pumpkin Seed Oil and Rapeseed Oil.Gels. 2024 Jun 5;10(6):384. doi: 10.3390/gels10060384. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38920930 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of different gelators on the physicochemical properties and microstructure of coconut oleogels.J Sci Food Agric. 2024 Jul;104(9):5139-5148. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13338. Epub 2024 Feb 7. J Sci Food Agric. 2024. PMID: 38284624
-
Ethylcellulose Oleogels: Structure, Functionality, and Food Applications.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2018;84:1-56. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2018. PMID: 29555066
-
Virgin coconut oil: A comprehensive review of antioxidant activity and mechanisms contributed by phenolic compounds.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(4):1052-1075. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2113361. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 35997296 Review.
-
Edible oleogels as solid fat alternatives: Composition and oleogelation mechanism implications.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2022 May;21(3):2077-2104. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12928. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2022. PMID: 35279947 Review.
Cited by
-
Numerical simulation and experimental validation of the oleogel formation from grape seed oil and beeswax.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 7;15(1):1213. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82352-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39774968 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the impact of zein microfibers on the physicochemical and microstructural properties of bi-gels based on ι-carrageenan hydrogels and beeswax oleogels.Curr Res Food Sci. 2025 Jan 21;10:100985. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.100985. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 39944918 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Characterization of Ethylcellulose Oleogels Based on Pumpkin Seed Oil and Rapeseed Oil.Gels. 2024 Jun 5;10(6):384. doi: 10.3390/gels10060384. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38920930 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative oleogels: Developing sustainable bioactive delivery systems for healthier foods production.Food Chem X. 2025 Jul 9;29:102768. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102768. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40704188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multicomponent Oleogels Prepared with High- and Low-Molecular-Weight Oleogelators: Ethylcellulose and Waxes.Foods. 2023 Aug 17;12(16):3093. doi: 10.3390/foods12163093. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37628092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bascuas S., Salvador A., Hernando I., Quiles A. Designing Hydrocolloid-Based Oleogels with High Physical, Chemical, and Structural Stability. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020;4:111. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.00111. - DOI
-
- Ismail N.A., Amin K.A.M., Razali M.H. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. Volume 440. IOP Publishing; Bristol, UK: 2018. Mechanical and Antibacterial Activities Study of Gellan Gum/Virgin Coconut Oil Film Embedded Norfloxacin; p. 012001. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

