Viscoelastic Behavior and Phase Structure of High-Content SBS-Modified Asphalt
- PMID: 35746051
- PMCID: PMC9229837
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14122476
Viscoelastic Behavior and Phase Structure of High-Content SBS-Modified Asphalt
Abstract
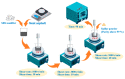
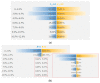
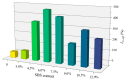
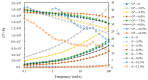
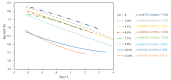
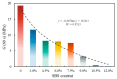
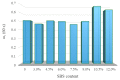
To investigate the effect of styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) modifier content on the viscoelastic behavior of SBS-modified asphalt (SBSMA) at different temperatures and phase structures, the star SBS modifier was chosen to fabricate seven types of SBSMA with different contents. Multiple stress creep recovery (MSCR), linear amplitude sweep (LAS), and low-temperature frequency sweep tests were adopted to study the influence of SBS modifier content on the viscoelastic performance of SBSMA at high to low temperatures. The SBSMA's microstructure with different contents was investigated using a fluorescence microscope. The results indicated that the change in non-recoverable creep compliance and creep recovery rate was bounded by 4.5% content at high temperatures, with an apparent turning point. The changing slope of content at less than 4.5% was much higher than that of the content greater than 4.5%. At medium temperatures, the fatigue life of SBSMA increased exponentially with the rising modifier content. The rate of increase in fatigue life was the largest as the content increased from 4.5% to 6.0%. At low temperatures, the low-temperature viscoelastic property index G (60 s) of SBSMA decreased logarithmically as the modifier content increased. In terms of the microscopic phase structure, the SBS modifier gradually changed from the dispersed to the continuous phase state with the increasing SBS modifier content.
Keywords: SBS; high-content polymer modified asphalt; phase structure; viscoelastic behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Sha A.M., Liu Z.Z., Jiang W., Qi L., Hu L.Q., Jiao W.X., Barbieri D.M. Advances and development trends in eco-friendly pavements. J. Road Eng. 2021;1:1–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jreng.2021.12.002. - DOI
-
- Jiang W., Yuan D.D., Shan J.H., Ye W.L., Lu H.H., Sha A.M. Experimental study of the performance of porous ultra-thin asphalt overlay. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022;23:2049–2061. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2020.1837826. - DOI
-
- Liu J.N., Zhang T.H., Guo H.Y., Wang Z.J., Wang X.F. Evaluation of self-healing properties of asphalt mixture containing steel slag under microwave heating: Mechanical, thermal transfer and voids microstructural characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2022;342:130932. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130932. - DOI
-
- Wang C.H., Wang M.H., Chen Q., Zhang L. Basic performance and asphalt smoke absorption effect of environment-friendly asphalt to improve pavement construction environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022;333:130142. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130142. - DOI
-
- Gao J., Yao Y.Q., Song L., Xu J., Yang J.G. Determining the maximum permissible content of recycled asphalt pavement stockpile in plant hot-mix recycled asphalt mixtures considering homogeneity: A case study in China. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022;16:e00961. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e00961. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 52122809/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 52038001/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 161072/Fok Ying-Tong Education Foundation
- 300203211215/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities-Excellent doctoral cultivation project of Chang'an University
- 202006560054/China Scholarship Council
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

