Voltammetric Behaviour of Rhodamine B at a Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode and Its Trace Determination in Environmental Water Samples
- PMID: 35746412
- PMCID: PMC9230127
- DOI: 10.3390/s22124631
Voltammetric Behaviour of Rhodamine B at a Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode and Its Trace Determination in Environmental Water Samples
Abstract
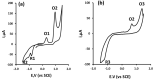
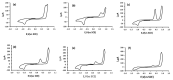
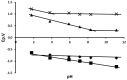
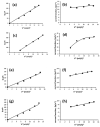
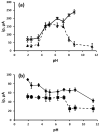
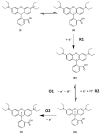
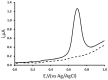
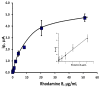
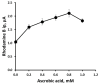
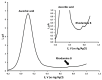
The voltammetric behaviour of Rhodamine B was studied at a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE), by cyclic and differential pulse voltammetry. Cyclic voltammograms exhibited two reduction peaks (designated R1 and R2) generated from the reduction of the parent compound through, first, one electron reduction (R1) to give a radical species, and then a further one-electron, one-proton reduction to give a neutral molecule (R2). On the reverse positive-going scan, two oxidation peaks were observed. The first, O1, resulted from the oxidation of the species generated at R2, and the second, O2, through the one-electron oxidation of the amine group. The nature of the redox reactions was further investigated by observing the effect of scan rate and pH on the voltammetric behaviour. The developed SPCE method was evaluated by carrying out Rhodamine B determinations on a spiked and unspiked environmental water sample. A mean recovery of 94.3% with an associated coefficient of variation of 2.9% was obtained. The performance characteristics indicated that reliable data may be obtained for Rhodamine B measurements in environmental water samples using this approach.
Keywords: Rhodamine B; screen-printed carbon electrode; voltammetry; water.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


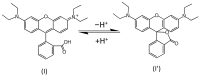
Similar articles
-
Voltammetric behaviour and trace determination of copper at a mercury-free screen-printed carbon electrode.Talanta. 2002 May 24;57(3):565-74. doi: 10.1016/s0039-9140(02)00060-7. Talanta. 2002. PMID: 18968656
-
Voltammetric behavior of nitrazepam and its determination in serum using liquid chromatography with redox mode dual-electrode detection.Anal Chem. 2006 Jan 15;78(2):416-23. doi: 10.1021/ac058035a. Anal Chem. 2006. PMID: 16408922
-
Sequential injection differential pulse voltammetric method based on screen printed carbon electrode modified with carbon nanotube/Nafion for sensitive determination of paraquat.Talanta. 2017 Aug 1;170:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.03.073. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Talanta. 2017. PMID: 28501144
-
Screen-Printed Voltammetric Sensors-Tools for Environmental Water Monitoring of Painkillers.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 22;22(7):2437. doi: 10.3390/s22072437. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35408052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origins of non-ideal behaviour in voltammetric analysis of redox-active monolayers.Nat Rev Chem. 2024 Aug;8(8):628-643. doi: 10.1038/s41570-024-00629-8. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Nat Rev Chem. 2024. PMID: 39039210 Review.
References
-
- Pubchem R.B. Use and Manufacturing. [(accessed on 22 April 2022)]; Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Rhodamine-B#section=Use-and-Ma....
-
- Abril J.M., Abdel-Aal M.M., Al-Gamal S.A., Abdel-Hay F.M., Zahar H.M. Marine Radioactivity Studies in the Suez Canal, Part II: Field Experiments and a Modelling Study of Dispersion. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000;50:503–514. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1999.0565. - DOI
-
- Jones C., Moller H., Hamilton W. A review of potential techniques for identifying individual stoats (Mustela erminea) visiting control or monitoring stations. N. Z. J. Zool. 2004;31:193–203. doi: 10.1080/03014223.2004.9518372. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

