A Single Dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine Elicits High Antibody Responses in Individuals with Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection Comparable to That of Two-Dose-Vaccinated, SARS-CoV-2-Infection-Naïve Individuals: A Longitudinal Study in Ethiopian Health Workers
- PMID: 35746467
- PMCID: PMC9229151
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10060859
A Single Dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine Elicits High Antibody Responses in Individuals with Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection Comparable to That of Two-Dose-Vaccinated, SARS-CoV-2-Infection-Naïve Individuals: A Longitudinal Study in Ethiopian Health Workers
Abstract
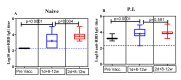
Single-dose COVID-19 vaccines, mostly mRNA-based vaccines, are shown to induce robust antibody responses in individuals who were previously infected with SARS-CoV-2, suggesting the sufficiency of a single dose for those individuals in countries with limited vaccine supply. However, these important data are limited to developed nations. We conducted a prospective longitudinal study among Ethiopian healthcare workers who received a ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine. We compared the geometric mean titers (GMTs) of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD)-specific IgG antibodies in 39 SARS-CoV-2 naïve participants and 24 participants previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 (P.I.), who received two doses of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine across the two post-vaccination time points (at 8 to 12 weeks post single dose and two dose vaccinations). We noted that the GMT (1632.16) in naïve participants at 8-12 weeks post first dose were comparable to the GMT (1674.94) observed in P.I. participants prior to vaccination. Interestingly, P.I. participants had significantly higher antibody titers compared to naïve participants, after both the first (GMT, 4913.50 vs. 1632.16) and second doses (GMT, 9804.60 vs. 6607.30). Taken together, our findings show that a single ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 dose in previously SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals elicits similar, if not higher, antibody responses to those of two-dose-vaccinated naïve individuals.
Keywords: ChAdOx1 nCoV-19; RBD; SARS-CoV-2; dose; naïve; prior infection; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Update of
-
A single dose ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine elicits high antibody responses in individuals with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection comparable to that of double dose vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 infection naïve individuals.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2022 Jan 11:rs.3.rs-1250175. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1250175/v1. Res Sq. 2022. Update in: Vaccines (Basel). 2022 May 27;10(6):859. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060859. PMID: 35043108 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Frater J., Ewer K.J., Ogbe A., Pace M., Adele S., Adland E., Alagaratnam J., Aley P.K., Ali M., Ansari M.A., et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 (AZD1222) Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in HIV Infection: A Single-Arm Substudy of a Phase 2/3 Clinical Trial. Lancet HIV. 2021;8:e474–e485. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00103-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xia S., Zhang Y., Wang Y., Wang H., Yang Y., Gao G.F., Tan W., Wu G., Xu M., Lou Z., et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine, BBIBP-CorV: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1/2 Trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21:39–51. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30831-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

