Evaluation of the Potency of the Pertussis Vaccine in Experimental Infection Model with Bordetella pertussis: Study of the Case of the Pertussis Vaccine Used in the Expanded Vaccination Program in Algeria
- PMID: 35746514
- PMCID: PMC9230502
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10060906
Evaluation of the Potency of the Pertussis Vaccine in Experimental Infection Model with Bordetella pertussis: Study of the Case of the Pertussis Vaccine Used in the Expanded Vaccination Program in Algeria
Abstract
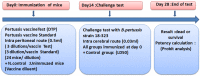
In Algeria, vaccination against pertussis is carried out using the whole-cell pertussis vaccine combined with the diphtheria and tetanus toxoids (DTwp). The quality control of vaccines locally produced or imported is carried out before the batch release. The aim of our work was to evaluate the potency of pertussis vaccines. In the present study, five consecutive trials of potency were conducted on samples of the same batch of (DTwp) using the mouse protection test (MPT) against experimental infection of Bordetella pertussis strain 18323, based on the Kendrick test. The virulence of B. pertussis strain 18-323 was verified by the mortality of mice, with an average LD50 of 338.92, as well as the dose of the lethal test containing a mean number of LD50 of 324.43. The (MPT) test recorded a relative potency of 8.02 IU/human dose, with 95% CL of (3.56-18.05) IU/human dose. The development of the (MPT) at the laboratory of quality control of vaccines and sera at the Pasteur Institute of Algeria was effective in evaluating the potency of whole-cell pertussis vaccines. Interestingly, our study indicates that this potency is necessary for the vaccine quality assurance. Further validation is needed to strengthen the application and routine use of the test.
Keywords: Algeria; Bordetella pertussis; Kendrick test; LD50; relative potency; whole-cell pertussis vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dias W., Raw I. Pertussis: Disease, Control and Challenges. BoD–Books on Demand; Norderstedt, Germany: 2018.
-
- Stefanelli P. Pertussis Infection and Vaccines. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2019. Pertussis: Identification, prevention and control; pp. 127–136. - PubMed
-
- Lazri M., Caro V., Brun D., Njamkepo E., Ouraghi R. La coqueluche en Algérie: Diagnostic direct et indirect de l’infection, sensibilité aux antibiotiques des souches identifiées. L’institut Pasteur D’algérie. 2008;66:29.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

