Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Hospitalized Patients Treated with Remdesivir: A Nationwide, Registry-Based Study in Italy
- PMID: 35746668
- PMCID: PMC9228114
- DOI: 10.3390/v14061197
Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Hospitalized Patients Treated with Remdesivir: A Nationwide, Registry-Based Study in Italy
Abstract
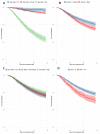
Remdesivir is the first drug approved for treatment of COVID-19 but current evidence for recommending its use for the treatment of moderate-to-severe disease is still controversial among clinical guidelines. We performed a nationwide, registry-based study including all Italian hospitalized patients with COVID-19 treated with remdesivir to assess the impact of major confounders on crude 15-day and 29-day mortality. Mortality was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier estimator and the Cox proportional-hazards model was applied to analyze the risks by patient's baseline features. In total, 16,462 patients treated with remdesivir from 29 October 2020 to 17 December 2020 were entered in the study. Crude 15-day and 29-day mortality were 7.1% (95% CI, 6.7-7.5%) and 11.7% (95% CI, 11.2-12.2%), respectively. Being treated within two days of admission reduced the risk of death by about 40% (HR 1.4, 95% CI, 1.2-1.6). Results from the largest cohort of remdesivir-treated patients suggests that mortality in SARS-CoV-2 hospitalized patients is substantially influenced by the days between SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis and drug prescription. Current recommendations and future clinical trials for remdesivir alone or in combination should carefully consider the target population and timing for best efficacy of treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; RWE; mortality; remdesivir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests regarding this article. The views expressed in this work are personal and may not be understood or quoted as being made on behalf of or reflective of the position of the Italian Medicines Agency or of one of their committees or working parties.
Figures

References
-
- Sheahan T.P., Sims A.C., Leist S.R., Schäfer A., Won J., Brown A.J., Montgomery S.A., Hogg A., Babusis D., Clarke M.O., et al. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:222. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13940-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

