Biological Characteristics of Infectious Laryngotracheitis Viruses Isolated in China
- PMID: 35746670
- PMCID: PMC9227991
- DOI: 10.3390/v14061200
Biological Characteristics of Infectious Laryngotracheitis Viruses Isolated in China
Abstract
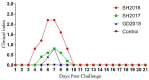
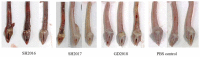
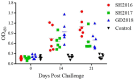
Infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) causes severe respiratory disease in chickens and results in huge economic losses in the poultry industry worldwide. To correlate the genomic difference with the replication and pathogenicity, phenotypes of three ILTVs isolated from chickens in China from 2016 to 2018 were sequenced by high-throughput sequencing. Based on the entire genome, the isolates GD2018 and SH2017 shared 99.9% nucleotide homology, while the isolate SH2016 shared 99.7% nucleotide homology with GD2018 and SH2017, respectively. Each virus genome contained 82 ORFs encoding 77 kinds of protein, 31 of which share the same amino acid sequence in the three viruses. GD2018 and SH2017 shared 57 proteins with the same amino acid sequence, while SH2016 shared 42 and 41 proteins with the amino acid sequences of GD2018 and SH2017, respectively. SH2016 propagated efficiently in allantoic fluid and on chorioallantoic membranes (CAMs) of SPF chicken embryo eggs, while GD2018 and SH2017 proliferated well only on CAMs. GD2018 propagated most efficiently on CAMs and LMH cells among three isolates. SH2016 caused serious clinical symptoms, while GD2018 and SH2017 caused mild and moderate clinical symptoms in chickens, although the sero of the chickens infected with those three isolates were all positive for anti-ILTV antibody at 14 and 21 days after challenge. Three ILTVs with high genetic homology showed significant differences in the replication in different culture systems and the pathogenicity of chickens, providing basic materials for studying the key determinants of pathogenicity of ILTV.
Keywords: biological characteristics; genome; infectious laryngotracheitis virus; pathogenicity; replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with this manuscript.
Figures


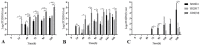
Similar articles
-
Pathogenic and Transmission Potential of Wildtype and Chicken Embryo Origin (CEO) Vaccine Revertant Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus.Viruses. 2021 Mar 24;13(4):541. doi: 10.3390/v13040541. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33805117 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative full genome sequence analysis of wild-type and chicken embryo origin vaccine-like infectious laryngotracheitis virus field isolates from Canada.Infect Genet Evol. 2022 Oct;104:105350. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2022.105350. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Infect Genet Evol. 2022. PMID: 35977653
-
Isolation, identification, molecular and pathogenicity characteristics of an infectious laryngotracheitis virus from Hubei province, China.Poult Sci. 2024 Feb;103(2):103271. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.103271. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38064882 Free PMC article.
-
The route of inoculation dictates the replication patterns of the infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) pathogenic strain and chicken embryo origin (CEO) vaccine.Avian Pathol. 2017 Dec;46(6):585-593. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2017.1331029. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Avian Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28532159 Review.
-
Immune responses to infectious laryngotracheitis virus.Dev Comp Immunol. 2013 Nov;41(3):454-62. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.03.022. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23567343 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of respiratory syndromes in poultry: pathogens, prevention, and control measures.Vet Res. 2025 May 17;56(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01506-y. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40382667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a single-cycle replication recombinant infectious laryngotracheitis virus lacking the glycoprotein H gene and evaluation of its role in viral entry and infectivity.Arch Virol. 2025 Apr 29;170(6):115. doi: 10.1007/s00705-025-06302-9. Arch Virol. 2025. PMID: 40299141
-
Molecular characteristics and pathogenicity analysis of infectious laryngotracheitis virus isolated in China from 2015 to 2019.Poult Sci. 2025 Feb;104(2):104751. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104751. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39754926 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a recombinant infectious bronchitis virus vaccine expressing infectious laryngotracheitis virus multiple epitopes.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104578. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104578. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39671857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King A., Carstens E.B., Lefkowitz E.J. Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2011.
-
- May H.G., Tittsler R.P. Tracheolaryngitis in poultry. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1996;40:494–500.
-
- Koski D.M., Predgen A.S., Trampel D.W., Conrad S.K., Narwold D.R., Hermann J.R. Comparison of the pathogenicity of the USDA challenge virus strain to a field strain of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Biologicals J. Int. Assoc. Biol. Standardizat. 2015;43:232–237. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2015.05.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nazir S., Yegoraw A.A., Charlesworth R.P.G., Williamson S., Sharpe S., Walkden-Brown S.W., Gerber P.F. Marked differences in virulence of three Australian field isolates of infectious laryngotracheitis virus in meat and layer chickens. Avian Pathol. 2020;49:600–610. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2020.1801987. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

