EGR1 Upregulation during Encephalitic Viral Infections Contributes to Inflammation and Cell Death
- PMID: 35746681
- PMCID: PMC9227295
- DOI: 10.3390/v14061210
EGR1 Upregulation during Encephalitic Viral Infections Contributes to Inflammation and Cell Death
Abstract
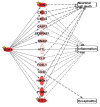
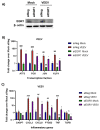
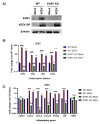
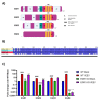
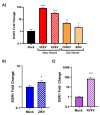
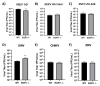
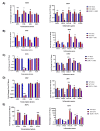
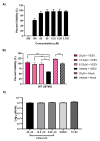
Early growth response 1 (EGR1) is an immediate early gene and transcription factor previously found to be significantly upregulated in human astrocytoma cells infected with Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV). The loss of EGR1 resulted in decreased cell death but had no significant impact on viral replication. Here, we extend these studies to determine the impacts of EGR1 on gene expression following viral infection. Inflammatory genes CXCL3, CXCL8, CXCL10, TNF, and PTGS2 were upregulated in VEEV-infected cells, which was partially dependent on EGR1. Additionally, transcription factors, including EGR1 itself, as well as ATF3, FOS, JUN, KLF4, EGR2, and EGR4 were found to be partially transcriptionally dependent on EGR1. We also examined the role of EGR1 and the changes in gene expression in response to infection with other alphaviruses, including eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV), Sindbis virus (SINV), and chikungunya virus (CHIKV), as well as Zika virus (ZIKV) and Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV), members of the Flaviviridae and Phenuiviridae families, respectively. EGR1 was significantly upregulated to varying degrees in EEEV-, CHIKV-, RVFV-, SINV-, and ZIKV-infected astrocytoma cells. Genes that were identified as being partially transcriptionally dependent on EGR1 in infected cells included ATF3 (EEEV, CHIKV, ZIKV), JUN (EEEV), KLF4 (SINV, ZIKV, RVFV), CXCL3 (EEEV, CHIKV, ZIKV), CXCL8 (EEEV, CHIKV, ZIKV, RVFV), CXCL10 (EEEV, RVFV), TNF-α (EEEV, ZIKV, RVFV), and PTGS2 (EEEV, CHIKV, ZIKV). Additionally, inhibition of the inflammatory gene PTGS2 with Celecoxib, a small molecule inhibitor, rescued astrocytoma cells from VEEV-induced cell death but had no impact on viral titers. Collectively, these results suggest that EGR1 induction following viral infection stimulates multiple inflammatory mediators. Managing inflammation and cell death in response to viral infection is of utmost importance, especially during VEEV infection where survivors are at-risk for neurological sequalae.
Keywords: EGR1; Venezuelan equine encephalitis; alphaviruses; astrocytes; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
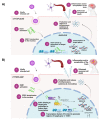
Similar articles
-
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus Induces Apoptosis through the Unfolded Protein Response Activation of EGR1.J Virol. 2016 Jan 20;90(7):3558-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02827-15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26792742 Free PMC article.
-
EGR1 upregulation following Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infection is regulated by ERK and PERK pathways contributing to cell death.Virology. 2020 Jan 2;539:121-128. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2019.10.016. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Virology. 2020. PMID: 31733451 Free PMC article.
-
PERK Is Critical for Alphavirus Nonstructural Protein Translation.Viruses. 2021 May 12;13(5):892. doi: 10.3390/v13050892. Viruses. 2021. Retraction in: Viruses. 2025 Feb 26;17(3):318. doi: 10.3390/v17030318. PMID: 34065980 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Understanding host responses to equine encephalitis virus infection: implications for therapeutic development.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022 Dec;20(12):1551-1566. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2022.2141224. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022. PMID: 36305549 Review.
-
Advances in the Development of Small Molecule Antivirals against Equine Encephalitic Viruses.Viruses. 2023 Feb 1;15(2):413. doi: 10.3390/v15020413. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851628 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of lncRNA Expression Pattern and Potential Role in Heart Failure Pathology.Dis Markers. 2023 Jul 12;2023:2369352. doi: 10.1155/2023/2369352. eCollection 2023. Dis Markers. 2023. PMID: 37476628 Free PMC article.
-
Egr-1 is a key regulator of the blood-brain barrier damage induced by meningitic Escherichia coli.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 17;22(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01488-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38233877 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Changes in Glioma Cells upon Infection with the Oncolytic Virus VV-GMCSF-Lact.Cells. 2023 Nov 12;12(22):2616. doi: 10.3390/cells12222616. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37998351 Free PMC article.
-
Early Growth Response Factor 4 (EGR4) Expression in Gut Tissues and Regional Lymph Nodes of Cattle with Different Types of Paratuberculosis-Associated Lesions: Potential Role of EGR4 in Resilience to Paratuberculosis.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;15(7):1012. doi: 10.3390/ani15071012. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218405 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathogenesis of Encephalitic Alphaviruses in Non-Human Primate and Mouse Models of Infection.Pathogens. 2025 Feb 14;14(2):193. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14020193. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40005568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paredes A., Weaver S., Watowich S., Chiu W. Structural biology of old world and new world alphaviruses. Arch. Virol. Suppl. 2005;19:179–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

