New p35 (H3L) Epitope Involved in Vaccinia Virus Neutralization and Its Deimmunization
- PMID: 35746695
- PMCID: PMC9227246
- DOI: 10.3390/v14061224
New p35 (H3L) Epitope Involved in Vaccinia Virus Neutralization and Its Deimmunization
Abstract
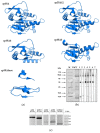
Vaccinia virus (VACV) is a promising oncolytic agent because it exhibits many characteristic features of an oncolytic virus. However, its effectiveness is limited by the strong antiviral immune response induced by this virus. One possible approach to overcome this limitation is to develop deimmunized recombinant VACV. It is known that VACV p35 is a major protein for B- and T-cell immune response. Despite the relevance of p35, its epitope structure remains insufficiently studied. To determine neutralizing epitopes, a panel of recombinant p35 variants was designed, expressed, and used for mice immunization. Plaque-reduction neutralization tests demonstrated that VACV was only neutralized by sera from mice that were immunized with variants containing both N- and C- terminal regions of p35. This result was confirmed by the depletion of anti-p35 mice sera with recombinant p35 variants. At least nine amino acid residues affecting the immunogenic profile of p35 were identified. Substitutions of seven residues led to disruption of B-cell epitopes, whereas substitutions of two residues resulted in the recognition of the mutant p35 solely by non-neutralizing antibodies.
Keywords: H3L; deimmunization; epitope; immunogenicity; neutralizing antibodies; oncolytic vaccinia virus; oncolytic virus; orthopoxvirus; p35; vaccinia virus.
Conflict of interest statement
All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and the order of authors, and there is no financial interest to report. All co-authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Moss B. Poxviridae. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., editors. Fields Virology. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2013. pp. 2129–2159.
-
- MacNeil A., Reynolds M.G., Carroll D.S., Karem K., Braden Z., Lash R., Moundeli A., Mombouli J.-V., Jumaan A.O., Schmid D.S., et al. Monkeypox or Varicella? Lessons from a Rash Outbreak Investigation in the Republic of the Congo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009;80:503–507. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2009.80.503. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

