Shiftless, a Critical Piece of the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection
- PMID: 35746809
- PMCID: PMC9230503
- DOI: 10.3390/v14061338
Shiftless, a Critical Piece of the Innate Immune Response to Viral Infection
Abstract
Since its initial characterization in 2016, the interferon stimulated gene Shiftless (SHFL) has proven to be a critical piece of the innate immune response to viral infection. SHFL expression stringently restricts the replication of multiple DNA, RNA, and retroviruses with an extraordinary diversity of mechanisms that differ from one virus to the next. These inhibitory strategies include the negative regulation of viral RNA stability, translation, and even the manipulation of RNA granule formation during viral infection. Even more surprisingly, SHFL is the first human protein found to directly inhibit the activity of the -1 programmed ribosomal frameshift, a translation recoding strategy utilized across nearly all domains of life and several human viruses. Recent literature has shown that SHFL expression also significantly impacts viral pathogenesis in mouse models, highlighting its in vivo efficacy. To help reconcile the many mechanisms by which SHFL restricts viral replication, we provide here a comprehensive review of this complex ISG, its influence over viral RNA fate, and the implications of its functions on the virus-host arms race for control of the cell.
Keywords: C19ORF66; FLJ11286; IRAV; ISG; RNA granules; RNA stability; RyDEN; SVA-1; innate immune response; ribosomal frameshift; shiftless; translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
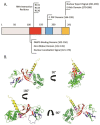
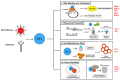
References
-
- Gaucher D., Therrien R., Kettaf N., Angermann B.R., Boucher G., Filali-Mouhim A., Moser J.M., Mehta R.S., Drake D.R., III, Castro E., et al. Yellow fever vaccine induces integrated multilineage and polyfunctional immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 2008;205:3119–3131. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082292. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kash J.C., Mühlberger E., Carter V., Grosch M., Perwitasari O., Proll S.C., Thomas M.J., Weber F., Klenk H.-D., Katze M.G. Global suppression of the host antiviral response by Ebola-and Marburgviruses: Increased antagonism of the type I interferon response is associated with enhanced virulence. J. Virol. 2006;80:3009–3020. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.6.3009-3020.2006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

