Extract of Xylopia aethiopica and its kaurene diterpene, xylopic acid, improve learning and memory in mice
- PMID: 35746979
- PMCID: PMC9210480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.03.006
Extract of Xylopia aethiopica and its kaurene diterpene, xylopic acid, improve learning and memory in mice
Abstract
Background: Cognitive dysfunction, presenting as learning and memory impairment, is a common manifestation in many chronic diseases of the nervous system. Some of these diseases include depression, epilepsy, and Alzheimer's disease. To date, few drugs or medicinal products have shown ability to improve learning and memory deficits. Neuroprotection is one of the mechanisms by which memory could be improved. The extract of Xylopia aethiopica and its kaurene derivative, xylopic acid, have previously demonstrated neuroprotective effects in animal models. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of an extract of Xylopia aethiopica fruit and xylopic acid, on learning and memory using murine models.
Materials and methods: Unripe Xylopia aethiopica fruits were collected, dried, and extracted using 70% v/v ethanol. Xylopic acid was isolated from the fruits using petroleum ether, concentrated with ethyl acetate and then recrystallized with petroleum ether before purifying with ethanol (96%v/v). Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice received oral doses of the extract of Xylopia aethiopica (XAE; 30, 100 and 300 mg/kg), xylopic acid (XA; 30, 100 and mg/kg), citicoline (300 mg/kg), piracetam (300 mg/kg) or ketamine (30 mg/kg) and saline (vehicle). The animals were then taken through the Morris water maze test (MWM), spontaneous alternation Y-maze test (Y-maze), and novel object recognition test (NOR), to assess learning and memory.
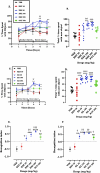
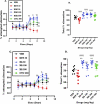
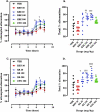
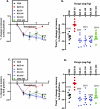
Results: In the NOR test, XAE (30, 100 and 300 mg/kg) and XA (30, 100 and 300 mg/kg) increased the percentage exploration and recognition index (p = 0.0005 and p < 0.0001, respectively) when compared to both vehicle and ketamine groups. Similarly, doses of XAE and XA as used in the NOR test increased the percentage alternation in the Y-maze test. Although XAE and XA treatments decreased the latencies to find hidden platform in the MWM test, it was not significantly different from the vehicle group. However, this decrease in latency differed significantly when compared to the ketamine group. Interestingly, both XAE and XA treatments increased the percentage frequency to the target quadrant in the probe trial of the MWM. It is noteworthy that in all the three models used, both the extract and xylopic acid performed better than piracetam and citicoline, the reference drugs.
Conclusion: The ethanolic extract of Xylopia aethiopica fruit and xylopic acid improved exploratory learning and recognition memory, spatial working, recognition, and reference memories in the behavioral tests.
Keywords: AUC, Area under the curve; CTC, Citicoline; HPLC, High performance liquid chromatography; ICR, Institute of Cancer Research; KET, Ketamine; MWM, Morris water maze; Morris water maze; NOR, Novelty object recognition; Nootropic; Novelty object recognition; PCT, Piracetam; Spontaneous alternation Y-maze; TLC, Thin layer chromatography; VEH, Vehicle; XA, Xylopic acid; XAE, Extract of Xylopia aethiopica; Xylopia aethiopica; Xylopic acid; Y-maze, Spontaneous alternation Y-maze.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of Herb-Drug Interactions between Xylopia aethiopica, Its Principal Constituent Xylopic Acid, and Antidepressants.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 May 25;2024:9923801. doi: 10.1155/2024/9923801. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38826835 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of an ethanol extract and the diterpene, xylopic acid, of Xylopia aethiopica fruits in murine models of musculoskeletal pain.Pharm Biol. 2016 Dec;54(12):2978-2986. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1199040. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Pharm Biol. 2016. PMID: 27430751
-
Analgesic effects of an ethanol extract of the fruits of Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) A. Rich (Annonaceae) and the major constituent, xylopic acid in murine models.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2012 Oct;4(4):291-301. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.103251. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2012. PMID: 23248562 Free PMC article.
-
Orofacial pain models induce impairment in spatial learning and working memory in rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 5;988:177225. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177225. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39740736
-
The effect of silver nanoparticles on learning and memory in rodents: "a systematic review".J Occup Med Toxicol. 2023 Aug 1;18(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12995-023-00381-7. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37525184 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Duguetia furfuracea (A.ST. Hil.) Saff.: Neuroprotective Effect on Chemically Induced Amnesia, Anxiolytic Effects and Preclinical Safety Evaluation in Mice.Biology (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;13(12):981. doi: 10.3390/biology13120981. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765648 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic and Curative Potency of Xylopia aethiopica "(Dunal) A. Rich." Leaf Extract on Mice Malaria Parasite (Plasmodium berghei).Acta Parasitol. 2025 Jul 8;70(4):152. doi: 10.1007/s11686-025-01095-y. Acta Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40627280
-
Sex Dimorphism in Pain Threshold and Neuroinflammatory Response: The Protective Effect of Female Sexual Hormones on Behavior and Seizures in an Allergic Rhinitis Model.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 23;19(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10114-0. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38652402
-
Elucidating the monoamine oxidase B inhibitory effect of kaurene diterpenoids from Xylopia aethiopica: An in silico approach.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 27;19(11):e0308021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308021. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2025 May 8;20(5):e0324095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324095. PMID: 39602408 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Anjula S., Sarvesh S., Hemant S., Pratap S., Dheeraj K., Amod K.S., Rajendra N. a, Rakesh K.D. An experimental study to evaluate the effect of mucuna pruriens on learning and memory in mice. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 2015;4(4):144–148.
-
- Baldi E., Efoudebe M., Lorenzini C.A., Bucherelli C. Spatial navigation in the Morris water maze: working and long lasting reference memories. Neurosci. Lett. 2005;378:176–180. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
