Electrochemical reduction of CO2 in the captured state using aqueous or nonaqueous amines
- PMID: 35747389
- PMCID: PMC9209719
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104558
Electrochemical reduction of CO2 in the captured state using aqueous or nonaqueous amines
Abstract
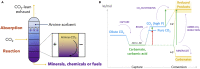
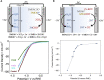
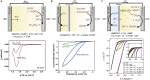
CO2 capture and its electrochemical conversion have historically developed as two distinct technologies and scientific fields. Each process possesses unique energy penalties, inefficiencies, and costs, which accrue along the mitigation pathway from emissions to product. Recently, the concept of integrating CO2 capture and electrochemical conversion, or "electrochemically reactive capture," has aroused attention following early laboratory-scale proofs-of-concept. However, the integration of the two processes introduces new complexities at a basic science and engineering level, many of which have yet to be clearly defined. The key parameters to guide reaction, electrolyte, electrode, and system design would, therefore, benefit from delineation. To begin this effort, this perspective outlines several crucial physicochemical and electrochemical considerations, where we argue that the absence of basic knowledge leaves the field of designing metaphorically in the dark. The considerations make clear that there is ample need for fundamental science that can better inform design, following which the potential impacts of integration can be rigorously assessed beyond what is possible at present.
Keywords: chemistry; electrochemical energy conversion; electrochemistry; engineering.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Abdinejad M., Mirza Z., Zhang X.a., Kraatz H.B. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of primary amines for CO2 reduction using copper electrodes in aqueous solution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020;8:1715–1720. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06837. - DOI
-
- Ahmad N., Wang X., Sun P., Chen Y., Rehman F., Xu J., Xu X. Electrochemical CO2 reduction to CO facilitated by MDEA-based deep eutectic solvent in aqueous solution. Renew. Energy. 2021;177:23–33. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.05.106. - DOI
-
- Azizi S. Evaluation of mass transfer resistance across the interface for CO2–propylene carbonate system: experimental and mathematical modeling. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019;149:34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2019.07.005. - DOI
-
- Bernhardsen I.M., Knuutila H.K. A review of potential amine solvents for CO2 absorption process: absorption capacity, cyclic capacity and pKa. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2017;61:27–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2017.03.021. - DOI
-
- Bhattacharya M., Sebghati S., Vanderlinden R.T., Saouma C.T. Toward combined carbon capture and recycling: addition of an amine alters product selectivity from CO to formic acid in manganese catalyzed reduction of CO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020;142:17589–17597. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c07763. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

