Plasma Levels of Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator (tPA) in Normal Aging and Alzheimer's Disease: Links With Cognition, Brain Structure, Brain Function and Amyloid Burden
- PMID: 35747448
- PMCID: PMC9211060
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.871214
Plasma Levels of Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator (tPA) in Normal Aging and Alzheimer's Disease: Links With Cognition, Brain Structure, Brain Function and Amyloid Burden
Abstract
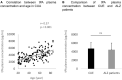
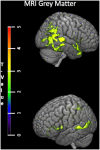
Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) is a protease known for its fibrinolytic action but is also involved in physiological and pathophysiological aging processes; including amyloid elimination and synaptic plasticity. The aim of the study was to investigate the role of tPA in cognitive and brain aging. Therefore, we assessed the links between tPA plasma concentration and cognition, structural MRI, FDG-PET and Flobetapir-PET neuroimaging in 155 cognitively unimpaired adults (CUA, aged 20-85 years old) and 32 patients with Alzheimer's disease (ALZ). A positive correlation was found between tPA and age in CUA (p < 0.001), with males showing higher tPA than females (p = 0.05). No significant difference was found between ALZ patients and cognitively unimpaired elders (CUE). Plasma tPA in CUA negatively correlated with global brain volume. No correlation was found with brain FDG metabolism or amyloid deposition. Age-related tPA changes were associated to changes in blood pressure, glycemia and body mass index. Within the ALZ patients, tPA didn't correlate with any cognitive or neuroimaging measures, but only with physiological measures. Altogether our study suggests that increased tPA plasma concentration with age is related to neuronal alterations and cardiovascular risk factors.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; FDG-PET; Flobetapir-PET; MRI; biological markers; cognition; normal aging; tissue plasminogen activator.
Copyright © 2022 Tomadesso, de Lizarrondo, Ali, Landeau, Mézenge, Perrotin, de La Sayette, Vivien and Chételat.
Conflict of interest statement
AP currently works for Life Molecular Imaging GmbH, Berlin, Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akhter H., Huang W.-T., van Groen T., Kuo H.-C., Miyata T., Liu R.-M. (2018). A small molecule inhibitor of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 reduces brain amyloid-β load and improves memory in an animal model of Alzheimer's Disease. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 64, 447–457. 10.3233/JAD-180241 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asselbergs F. W., Williams S. M., Hebert P. R., Coffey C. S., Hillege H. L., Navis G., et al. (2007). Gender-specific correlations of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and tissue plasminogen activator levels with cardiovascular disease-related traits. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5, 313–320. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02311.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benchenane K., Berezowski V., Ali C., Fernandez-Monreal M., Lopez-Atalaya J. P., Brillault J., et al. (2005). Tissue-type plasminogen activator crosses the intact blood-brain barrier by LDL-receptor related protein-mediated transcytosis. Circulation. 5:11. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000163542.48611.A2 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

