COVID-19-associated Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in CSF
- PMID: 35747763
- PMCID: PMC8899835
- DOI: 10.1177/19418744221079145
COVID-19-associated Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in CSF
Abstract
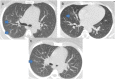
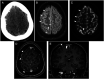
COVID-19 has been associated with central nervous system manifestations; however, cerebral venous thrombosis is rarely reported. A 34-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital with headache and recurrent seizures; she was recently discharged after COVID-19 pneumonia. Cranial magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance venography showed cortical vein thrombosis in the right frontal lobe. SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected in cerebrospinal fluid analysis. The patient was anticoagulated and put on antiepileptics. The most probable mechanism underlying the venous thrombosis is COVID-19-associated hypercoagulability. However, the relation between the viral RNA in cerebrospinal fluid analysis and the thrombosis is controversial.
Keywords: COVID-19; intracranial sinus thrombosis; seizures.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
