Medulloblastoma and the DNA Damage Response
- PMID: 35747808
- PMCID: PMC9209741
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.903830
Medulloblastoma and the DNA Damage Response
Abstract
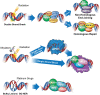
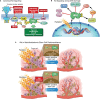
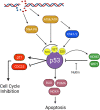
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most common malignant brain tumor in children with standard of care consisting of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Recent molecular profiling led to the identification of four molecularly distinct MB subgroups - Wingless (WNT), Sonic Hedgehog (SHH), Group 3, and Group 4. Despite genomic MB characterization and subsequent tumor stratification, clinical treatment paradigms are still largely driven by histology, degree of surgical resection, and presence or absence of metastasis rather than molecular profile. Patients usually undergo resection of their tumor followed by craniospinal radiation (CSI) and a 6 month to one-year multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen. While there is clearly a need for development of targeted agents specific to the molecular alterations of each patient, targeting proteins responsible for DNA damage repair could have a broader impact regardless of molecular subgrouping. DNA damage response (DDR) protein inhibitors have recently emerged as targeted agents with potent activity as monotherapy or in combination in different cancers. Here we discuss the molecular underpinnings of genomic instability in MB and potential avenues for exploitation through DNA damage response inhibition.
Keywords: medulloblastoma; p53 status; pediatrics; radiation oncology; therapeutic targeting.
Copyright © 2022 McSwain, Parwani, Shahab, Hambardzumyan, MacDonald, Spangle and Kenney.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M, Jones DTW, Schlanstein M, Northcott PA, et al. . Molecular Subgroups of Medulloblastoma: An International Meta-Analysis of Transcriptome, Genetic Aberrations, and Clinical Data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 Medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol (2012) 123(4):473–84. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-0958-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

