BMI as a predictor of high fasting blood glucose among people living with HIV in the Asia-Pacific region
- PMID: 35748404
- PMCID: PMC9789206
- DOI: 10.1111/hiv.13351
BMI as a predictor of high fasting blood glucose among people living with HIV in the Asia-Pacific region
Abstract
Background: Non-Asian body mass index (BMI) classifications are commonly used as a risk factor for high fasting blood glucose (FBG). We investigated the incidence and factors associated with high FBG among people living with HIV in the Asia-Pacific region, using a World Health Organization BMI classification specific to Asian populations.
Methods: This study included people living with HIV enrolled in a longitudinal cohort study from 2003 to 2019, receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART), and without prior tuberculosis. BMI at ART initiation was categorized using Asian BMI classifications: underweight (<18.5 kg/m2 ), normal (18.5-22.9 kg/m2 ), overweight (23-24.9 kg/m2 ), and obese (≥25 kg/m2 ). High FBG was defined as a single post-ART FBG measurement ≥126 mg/dL. Factors associated with high FBG were analyzed using Cox regression models stratified by site.
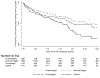
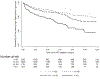
Results: A total of 3939 people living with HIV (63% male) were included. In total, 50% had a BMI in the normal weight range, 23% were underweight, 13% were overweight, and 14% were obese. Median age at ART initiation was 34 years (interquartile range 29-41). Overall, 8% had a high FBG, with an incidence rate of 1.14 per 100 person-years. Factors associated with an increased hazard of high FBG included being obese (≥25 kg/m2 ) compared with normal weight (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.79; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.31-2.44; p < 0.001) and older age compared with those aged ≤30 years (31-40 years: HR = 1.47; 95% CI 1.08-2.01; 41-50 years: HR = 2.03; 95% CI 1.42-2.90; ≥51 years: HR = 3.19; 95% CI 2.17-4.69; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: People living with HIV with BMI >25 kg/m2 were at increased risk of high FBG. This indicates that regular assessments should be performed in those with high BMI, irrespective of the classification used.
Keywords: Asia-Pacific; BMI; HIV; high fasting blood glucose.
© 2022 British HIV Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Disclosure Statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- GHO | By category | Raised fasting blood glucose (≥ 7.0 mmol/L or on medication)(age-standardized) - Estimates by WHO Region [Internet]. WHO. World Health Organization; [cited 2020 Mar 29]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/gho/data/view.main.NCDRGLUCAREGv?lang=en
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas [Internet]. [cited 2020 Mar 29]. Available from: https://idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabetes-atlas/13-diabet...
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global Prevalence of Diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004. May 1;27(5):1047–53. - PubMed
-
- HIV Basics | HIV/AIDS | CDC [Internet]. 2019. [cited 2020 Mar 29]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/index.html
-
- Noubissi EC, Katte JC, Sobngwi E. Diabetes and HIV. Curr Diab Rep. 2018. Oct 8;18(11):125. - PubMed