Photoaging: UV radiation-induced inflammation and immunosuppression accelerate the aging process in the skin
- PMID: 35748903
- PMCID: PMC9307547
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-022-01598-8
Photoaging: UV radiation-induced inflammation and immunosuppression accelerate the aging process in the skin
Abstract
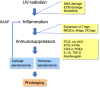
Background: Excessive exposure of the skin to UV radiation (UVR) triggers a remodeling of the immune system and leads to the photoaging state which is reminiscent of chronological aging. Over 30 years ago, it was observed that UVR induced an immunosuppressive state which inhibited skin contact hypersensitivity.
Methods: Original and review articles encompassing inflammation and immunosuppression in the photoaging and chronological aging processes were examined from major databases including PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar.
Results: Currently it is known that UVR treatment can trigger a cellular senescence and inflammatory state in the skin. Chronic low-grade inflammation stimulates a counteracting immunosuppression involving an expansion of immunosuppressive cells, e.g., regulatory T cells (Treg), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), and regulatory dendritic cells (DCreg). This increased immunosuppressive activity not only suppresses the function of effector immune cells, a state called immunosenescence, but it also induces bystander degeneration of neighboring cells. Interestingly, the chronological aging process also involves an accumulation of pro-inflammatory senescent cells and signs of chronic low-grade inflammation, called inflammaging. There is also clear evidence that inflammaging is associated with an increase in anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activities which promote immunosenescence.
Conclusion: It seems that photoaging and normal aging evoke similar processes driven by the remodeling of the immune system. However, it is likely that there are different molecular mechanisms inducing inflammation and immunosuppression in the accelerated photoaging and the chronological aging processes.
Keywords: Aging; Anti-inflammatory; Carcinogenesis; Lifespan; UVA; UVB.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

