Baicalein inhibits macrophage lipid accumulation and inflammatory response by activating the PPARγ/LXRα pathway
- PMID: 35749304
- PMCID: PMC9521661
- DOI: 10.1093/cei/uxac062
Baicalein inhibits macrophage lipid accumulation and inflammatory response by activating the PPARγ/LXRα pathway
Abstract
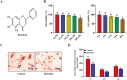
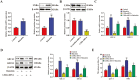
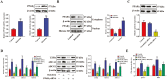
Lipid accumulation and inflammatory response are two major risk factors for atherosclerosis. Baicalein, a phenolic flavonoid widely used in East Asian countries, possesses a potential atheroprotective activity. However, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. This study was performed to explore the impact of baicalein on lipid accumulation and inflammatory response in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. Our results showed that baicalein up-regulated the expression of ATP binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1), ABCG1, liver X receptor α (LXRα), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), promoted cholesterol efflux, and inhibited lipid accumulation. Administration of baicalein also reduced the expression and secretion of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Knockdown of LXRα or PPARγ with siRNAs abrogated the effects of baicalein on ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression, cholesterol efflux, lipid accumulation as well as pro-inflammatory cytokine release. In summary, these findings suggest that baicalein exerts a beneficial effect on macrophage lipid accumulation and inflammatory response by activating the PPARγ/LXRα signaling pathway.
Keywords: LXRα; PPARγ; baicalein; inflammatory response; lipid accumulation.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Immunology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anti-atherosclerotic potential of baicalin mediated by promoting cholesterol efflux from macrophages via the PPARγ-LXRα-ABCA1/ABCG1 pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:257-264. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.06.046. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27389392
-
Propofol up-regulates expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, and SR-B1 through the PPARγ/LXRα signaling pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells.Cardiovasc Pathol. 2015 Jul-Aug;24(4):230-5. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2014.12.004. Epub 2014 Dec 27. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25600616
-
PLK1 promotes cholesterol efflux and alleviates atherosclerosis by up-regulating ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression via the AMPK/PPARγ/LXRα pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2022 Dec;1867(12):159221. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2022.159221. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2022. PMID: 35981705
-
Leonurine Prevents Atherosclerosis Via Promoting the Expression of ABCA1 and ABCG1 in a Pparγ/Lxrα Signaling Pathway-Dependent Manner.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(4):1703-1717. doi: 10.1159/000484031. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29045950
-
Allicin induces the upregulation of ABCA1 expression via PPARγ/LXRα signaling in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Jun;39(6):1452-1460. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2949. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28440421 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular protective effects of natural flavonoids on intestinal barrier injury.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;480(6):3343-3362. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05213-2. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39820766 Review.
-
Targeting Regulation of Macrophage to Treat Metabolic Disease: Role of Phytochemicals.Cell Prolif. 2025 Jul;58(7):e70012. doi: 10.1111/cpr.70012. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Cell Prolif. 2025. PMID: 40045164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between lipid metabolism and macrophages in atherosclerosis: therapeutic potential of natural products.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Mar 3;12:1529924. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1529924. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40099271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalein based nano-delivery system restores mitochondrial homeostasis through PPAR signaling pathway to promote wound healing in diabetes.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 19;23(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03427-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40383752 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Mechanism of Radix Paeoniae Rubra.-Cortex Moutan. Herb Pair in the Treatment of Atherosclerosis: A Work Based on Network Pharmacology and In Vitro Experiments.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Aug;24(8):800-817. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09881-2. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38951468
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

