Long term outcomes of patients with tuberculous meningitis: The impact of drug resistance
- PMID: 35749509
- PMCID: PMC9232145
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270201
Long term outcomes of patients with tuberculous meningitis: The impact of drug resistance
Abstract
Background: Little is known about the impact of drug-resistance on clinical outcomes among patients with tuberculosis meningitis (TBM).
Methods: A retrospective cohort study among patients treated for TBM in Tbilisi, Georgia. We performed medical chart abstraction to collect patient data. Long-term vital status was assessed using the Georgia National Death Registry. We utilized a Cox proportional-hazards model to evaluate the association of drug-resistance and mortality.
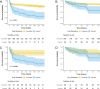
Results: Among 343 TBM suspects, 237 had a presentation consistent with TBM. Drug resistance was suspected (n = 5) or confirmed (n = 31) in 36 patients including 30 with multidrug- or rifampin-resistance and 6 with isoniazid-resistance. Thirty-four patients had HIV. The median follow-up time was 1331 days (IQR, 852-1767). Overall, 73 of 237 (30%) people died with 50 deaths occurring during and 23 after treatment. The proportion of death was higher among patients with drug-resistant vs. drug-susceptible disease (67% vs. 24%, p<0.001) and with HIV versus no HIV (59% vs 27%, p<0.001). Mortality was significantly higher in patients with drug-resistant TBM after 90 days of treatment (aHR = 7.2, CI95% [3.6-14.3], p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Mortality was high among patients with drug-resistant TBM with many deaths occurring post treatment. More effective treatment options are urgently needed for drug-resistant TBM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Chandir S, Hussain H, Salahuddin N, Amir M, Ali F, Lotia I, et al.. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis: a retrospective review of 194 cases at a tertiary care hospital in Karachi, Pakistan. J Pak Med Assoc. 2010;60(2):105–9. Epub 2010/03/10. . - PubMed
-
- Qian X, Nguyen DT, Lyu J, Albers AE, Bi X, Graviss EA. Risk factors for extrapulmonary dissemination of tuberculosis and associated mortality during treatment for extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018;7(1):102. Epub 2018/06/07. doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0106-1 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5988830. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

