FOXP3 exon 2 controls Treg stability and autoimmunity
- PMID: 35749515
- PMCID: PMC9333337
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abo5407
FOXP3 exon 2 controls Treg stability and autoimmunity
Abstract
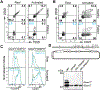
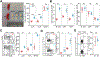
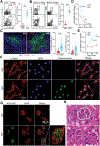
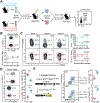
Differing from the mouse Foxp3 gene that encodes only one protein product, human FOXP3 encodes two major isoforms through alternative splicing-a longer isoform (FOXP3 FL) containing all the coding exons and a shorter isoform lacking the amino acids encoded by exon 2 (FOXP3 ΔE2). The two isoforms are naturally expressed in humans, yet their differences in controlling regulatory T cell phenotype and functionality remain unclear. In this study, we show that patients expressing only the shorter isoform fail to maintain self-tolerance and develop immunodeficiency, polyendocrinopathy, and enteropathy X-linked (IPEX) syndrome. Mice with Foxp3 exon 2 deletion have excessive follicular helper T (TFH) and germinal center B (GC B) cell responses, and develop systemic autoimmune disease with anti-dsDNA and antinuclear autoantibody production, as well as immune complex glomerulonephritis. Despite having normal suppressive function in in vitro assays, regulatory T cells expressing FOXP3 ΔE2 are unstable and sufficient to induce autoimmunity when transferred into Tcrb-deficient mice. Mechanistically, the FOXP3 ΔE2 isoform allows increased expression of selected cytokines, but decreased expression of a set of positive regulators of Foxp3 without altered binding to these gene loci. These findings uncover indispensable functions of the FOXP3 exon 2 region, highlighting a role in regulating a transcriptional program that maintains Treg stability and immune homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
FOXP3 splice variant is associated with autoimmune disease.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Sep;18(9):493. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00818-z. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35915337 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM, Hafler DA, FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10, 490–500 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M, Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 133, 775–787 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Curotto de Lafaille MA, Kutchukhidze N, Shen S, Ding Y, Yee H, Lafaille JJ, Adaptive Foxp3+ regulatory T cell-dependent and -independent control of allergic inflammation. Immunity 29, 114–126 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

