Fragment-based drug discovery-the importance of high-quality molecule libraries
- PMID: 35749608
- PMCID: PMC9627785
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13277
Fragment-based drug discovery-the importance of high-quality molecule libraries
Abstract
Fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD) is now established as a complementary approach to high-throughput screening (HTS). Contrary to HTS, where large libraries of drug-like molecules are screened, FBDD screens involve smaller and less complex molecules which, despite a low affinity to protein targets, display more 'atom-efficient' binding interactions than larger molecules. Fragment hits can, therefore, serve as a more efficient start point for subsequent optimisation, particularly for hard-to-drug targets. Since the number of possible molecules increases exponentially with molecular size, small fragment libraries allow for a proportionately greater coverage of their respective 'chemical space' compared with larger HTS libraries comprising larger molecules. However, good library design is essential to ensure optimal chemical and pharmacophore diversity, molecular complexity, and physicochemical characteristics. In this review, we describe our views on fragment library design, and on what constitutes a good fragment from a medicinal and computational chemistry perspective. We highlight emerging chemical and computational technologies in FBDD and discuss strategies for optimising fragment hits. The impact of novel FBDD approaches is already being felt, with the recent approval of the covalent KRASG12C inhibitor sotorasib highlighting the utility of FBDD against targets that were long considered undruggable.
Keywords: covalent fragments; fraglites; fragment library; fragment-based drug discovery; machine learning; virtual screening.
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

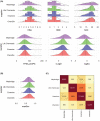
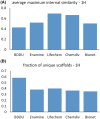
References
-
- Erlanson DA, Fesik SW, Hubbard RE, Jahnke W, Jhoti H. Twenty years on: the impact of fragments on drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15:605–19. - PubMed
-
- Wu G, Zhao T, Kang D, Zhang J, Song Y, Namasivayam V, et al. Overview of recent strategic advances in medicinal chemistry. J Med Chem. 2019;62:9375–414. - PubMed
-
- Murray CW, Newell DR, Angibaud P. A successful collaboration between academia, biotech and pharma led to discovery of Erdafitinib, a selective FGFR inhibitor recently approved by the FDA. MedChemComm. 2019;10:1509–11.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

