Parkinson's disease-risk protein TMEM175 is a proton-activated proton channel in lysosomes
- PMID: 35750034
- PMCID: PMC9236176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.05.021
Parkinson's disease-risk protein TMEM175 is a proton-activated proton channel in lysosomes
Abstract
Lysosomes require an acidic lumen between pH 4.5 and 5.0 for effective digestion of macromolecules. This pH optimum is maintained by proton influx produced by the V-ATPase and efflux through an unidentified "H+ leak" pathway. Here we show that TMEM175, a genetic risk factor for Parkinson's disease (PD), mediates the lysosomal H+ leak by acting as a proton-activated, proton-selective channel on the lysosomal membrane (LyPAP). Acidification beyond the normal range potently activated LyPAP to terminate further acidification of lysosomes. An endogenous polyunsaturated fatty acid and synthetic agonists also activated TMEM175 to trigger lysosomal proton release. TMEM175 deficiency caused lysosomal over-acidification, impaired proteolytic activity, and facilitated α-synuclein aggregation in vivo. Mutational and pH normalization analyses indicated that the channel's H+ conductance is essential for normal lysosome function. Thus, modulation of LyPAP by cellular cues may dynamically tune the pH optima of endosomes and lysosomes to regulate lysosomal degradation and PD pathology.
Keywords: Proton channel; acidification; degradation; lysosome; pH optimum.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.X. is the scientific co-founder and a partial owner of Lysoway Therapeutics Inc (Boston, MA).
Figures


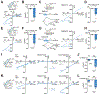

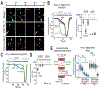
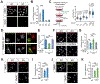
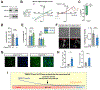
References
-
- Ashcom JD, and Jacobson LA (1989). Self-quenched fluorogenic protein substrates for the detection of cathepsin D and other protease activities. Analytical biochemistry 176, 261–264. - PubMed
-
- Ballabio A, and Bonifacino JS (2019). Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. - PubMed
-
- Blauwendraat C, Heilbron K, Vallerga CL, Bandres-Ciga S, von Coelln R, Pihlstrom L, Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Sharma M, Krohn L, et al. (2019). Parkinson’s disease age at onset genome-wide association study: Defining heritability, genetic loci, and alpha-synuclein mechanisms. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

