MicroRNAs in the development of potential therapeutic targets against COVID-19: A narrative review
- PMID: 35751930
- PMCID: PMC9221922
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.06.012
MicroRNAs in the development of potential therapeutic targets against COVID-19: A narrative review
Abstract
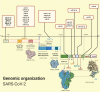
Background: As the therapeutic regimens against the COVID-19 remain scarce, the microRNAs (miRNAs) can be exploited to generate efficient therapeutic targets. The miRNAs have been found to play pivotal roles in the several regulatory functions influencing the prognosis of viral infection. The miRNAs have a prospective role in the up and down regulation of the ACE2 receptors. This review examines the clinical applications, as well as the possible threats associated with the use of miRNAs to combat the deleterious consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Methodology: This article was compiled to evaluate how the miRNAs are involved in the SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis and infection, and their potential functions which could help in the development of therapeutic targets against the COVID-19. The sources of the collected information include the several journals, databases and scientific search engines such as the Google scholar, Pubmed, Science direct, official website of WHO, among the other sites. The investigations on the online platform were conducted using the keywords miRNA biogenesis, miRNA and ACE2 interaction, therapeutic role of miRNAs against SARS-CoV-2 and miRNA therapy side effects.
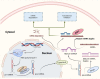
Results: This review has highlighted that the miRNAs can be exploited to generate potential therapeutic targets against the COVID-19. Changes in the miRNA levels following viral replication are an essential component of the host response to infection. The collection and modification of miRNA modulates may help to minimize the deleterious consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection, such as by controlling or inhibiting the generation of cytokines and chemokines. The degradation of viral RNA by the cellular miRNAs, along with the reduced expression of ACE2 receptors, can substantially reduce the viral load. Specific miRNAs have been found to have an antiviral influence, allowing the immune system to combat the infection or forcing the virus into a latency stage.
Conclusion: This review summarizes several studies revealing the involvement of miRNAs in diverse and complex processes during the infection process of SARS-CoV-2. The miRNAs can substantially reduce the viral load by degradation of viral RNA and reduced expression of ACE2 receptors, besides mitigating the deleterious consequences of the exaggerated secretion of cytokines. Extensive investigations need to be done by the scientific community to utilize the miRNA based strategies for the development of effective therapeutic targets against the COVID-19.
Keywords: ACE2 receptor; COVID-19; MiRNA; SARS-CoV-2; Therapeutics.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Maulud S.Q., Majed S.O., Ali B.A., Jalal P.J., Azeez S.H., Mohammad K.A. Epidemiological approach of SARS-CoV2 in the first month of appearance in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Eur J Mol Clin Med. 2020;7:2853–2865.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

