Machine-learning-optimized Cas12a barcoding enables the recovery of single-cell lineages and transcriptional profiles
- PMID: 35752172
- PMCID: PMC10599400
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.06.001
Machine-learning-optimized Cas12a barcoding enables the recovery of single-cell lineages and transcriptional profiles
Abstract
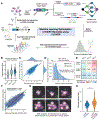
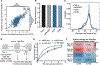
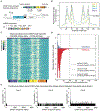
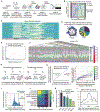
The development of CRISPR-based barcoding methods creates an exciting opportunity to understand cellular phylogenies. We present a compact, tunable, high-capacity Cas12a barcoding system called dual acting inverted site array (DAISY). We combined high-throughput screening and machine learning to predict and optimize the 60-bp DAISY barcode sequences. After optimization, top-performing barcodes had ∼10-fold increased capacity relative to the best random-screened designs and performed reliably across diverse cell types. DAISY barcode arrays generated ∼12 bits of entropy and ∼66,000 unique barcodes. Thus, DAISY barcodes-at a fraction of the size of Cas9 barcodes-achieved high-capacity barcoding. We coupled DAISY barcoding with single-cell RNA-seq to recover lineages and gene expression profiles from ∼47,000 human melanoma cells. A single DAISY barcode recovered up to ∼700 lineages from one parental cell. This analysis revealed heritable single-cell gene expression and potential epigenetic modulation of memory gene transcription. Overall, Cas12a DAISY barcoding is an efficient tool for investigating cell-state dynamics.
Keywords: CRISPR barcoding; Cas12a; PRC2; high throughput screening; lineage tracking; machine learning; melanoma; online learning optimization; single cell genomics; transcriptional memory.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Stanford University has filed patent applications with L.C. and N.W.H. as inventors on the basis of this work. L.C. is a member of the scientific advisory board of Arbor Biotechnologies.
Figures



References
-
- Abbasi-yadkori Y, Pál D, and Szepesvári C (2011). Improved Algorithms for Linear Stochastic Bandits. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst 24.
-
- Alemany A, Florescu M, Baron CS, Peterson-Maduro J, and van Oudenaarden A (2018). Whole-organism clone tracing using single-cell sequencing. Nature 556, 108–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

