Prognostic value of plasma level of superoxide dismutase in HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
- PMID: 35752786
- PMCID: PMC9233797
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-022-02371-1
Prognostic value of plasma level of superoxide dismutase in HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) is the most prevalent type of ACLF in China. The mortality rate of HBV-ACLF has decreased in recent years due to advances in treatment therapies; however, it is still above 50%. Many cases of HBV-ACLF are caused by HBV reactivation due to discontinuation of nucleoside analog treatment. The present study focused on plasma levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in HBV-ACLF patients and investigated whether the plasma level of SOD is a useful biomarker in assessing disease severity and predicting outcomes of HBV-ACLF patients, including patients treated with Entecavir (ETV) and patients who were withdrawn from ETV treatment.
Methods: Plasma samples and clinical data from 200 HBV-ACLF patients and from age- and sex-matched cirrhotic and healthy controls were collected and analyzed. Plasma levels of SOD were measured using an ELISA commercial kit.
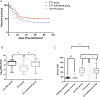
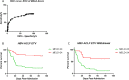
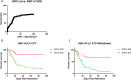
Results: Among the HBV-ACLF patients, in the ETV withdrawal group, the mortality rate was higher than in the ETV group (69.95% vs 46.71%, P < 0.05). Moreover, HBV-DNA and SOD plasma levels were higher in the ETV withdrawal group than in the ETV group (Log10(HBV-DNA): 6.49 ± 0.24 vs 4.79 ± 0.14, P < 0.01; SOD: 463.1 ± 27.61 U/mL vs 397.2 ± 10.97 U/mL, P < 0.05). The mortality and liver transplantation rates were significantly higher in HBV-ACLF patients with plasma levels of SOD > 428 U/mL than in patients with plasma SOD levels ≤ 428 U/mL.
Conclusions: Reactivation of HBV and elevated oxidative stress caused by discontinuation of ETV treatment are crucial factors in the pathogenesis of HBV-ACLF. Plasma level of SOD may serve as a useful biomarker in estimating disease severity and predicting outcomes of HBV-ACLF patients who stop ETV treatment.
Keywords: Acute on chronic liver failure; Entecavir; HBV; Prognosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of tenofovir alafenamide and entecavir for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Feb 28;47(2):194-201. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210578. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35545409 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Tenofovir Versus Entecavir for the Treatment of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure due to Reactivation of Chronic Hepatitis B With Genotypes B and C.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr;53(4):e171-e177. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001038. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 29659382
-
Is HBV viral load at admission associated with development of acute-on-chronic liver failure in patients with acute decompensation of chronic hepatitis B related cirrhosis?BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Apr 30;19(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-3988-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31039732 Free PMC article.
-
Acute-on-chronic liver failure in chronic hepatitis B: an update.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Apr;12(4):341-350. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2018.1426459. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29334786 Review.
-
Serum Interleukins as Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in HBV-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Sep 8;2022:7794890. doi: 10.1155/2022/7794890. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 36117587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and mortality in hepatic failure: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 28;25(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10783-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40155840 Free PMC article.
-
Early prediction of acute-on-chronic liver failure development in patients with diverse chronic liver diseases.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 15;14(1):28245. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79486-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39548240 Free PMC article.
-
Additive interaction between hepatitis B virus infection and tobacco smoking on the risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population.Infect Agent Cancer. 2025 Mar 20;20(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13027-025-00648-0. Infect Agent Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40114245 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Superoxide Dismutase Attenuates Hepatic Oxidative Stress in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through the Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Activation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 24;12(12):2040. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122040. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136160 Free PMC article.
-
SEMA6B induces macrophage-mediated inflammation and hepatocyte apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.Theranostics. 2024 Aug 19;14(13):5200-5218. doi: 10.7150/thno.97007. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39267780 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

